Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449
- PMID: 19726761
- PMCID: PMC5317279
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0902903
Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449
Abstract
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in children. Aberrant activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway is strongly implicated in the development of some cases of medulloblastoma. A 26-year-old man with metastatic medulloblastoma that was refractory to multiple therapies was treated with a novel hedgehog pathway inhibitor, GDC-0449; treatment resulted in rapid (although transient) regression of the tumor and reduction of symptoms. Molecular analyses of tumor specimens obtained before treatment suggested that there was activation of the hedgehog pathway, with loss of heterozygosity and somatic mutation of the gene encoding patched homologue 1 (PTCH1), a key negative regulator of hedgehog signaling.
2009 Massachusetts Medical Society
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

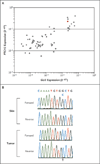
Comment in
-
Following the hedgehog to new cancer therapies.N Engl J Med. 2009 Sep 17;361(12):1202-5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe0906092. Epub 2009 Sep 2. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19726764 No abstract available.
References
-
- Crawford JR, MacDonald TJ, Packer RJ. Medulloblastoma in childhood: new biological advances. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:1073–1085. - PubMed
-
- Zeltzer PM, Boyett JM, Finlay JL, et al. Metastasis stage, adjuvant treatment, and residual tumor are prognostic factors for medulloblastoma in children: conclusions from the Children’s Cancer Group 921 randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:832–845. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, Placzek M. Orchestrating ontogenesis: variations on a theme by sonic hedgehog. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:841–850. - PubMed
-
- Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP. Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic hedgehog. Neuron. 1999;22:103–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
