Impaired endocytosis of the ion channel TRPM4 is associated with human progressive familial heart block type I
- PMID: 19726882
- PMCID: PMC2735920
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI38292
Impaired endocytosis of the ion channel TRPM4 is associated with human progressive familial heart block type I
Abstract
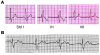
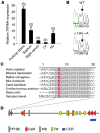
Progressive familial heart block type I (PFHBI) is a progressive cardiac bundle branch disease in the His-Purkinje system that exhibits autosomal-dominant inheritance. In 3 branches of a large South African Afrikaner pedigree with an autosomal-dominant form of PFHBI, we identified the mutation c.19G-->A in the transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 4 gene (TRPM4) at chromosomal locus 19q13.3. This mutation predicted the amino acid substitution p.E7K in the TRPM4 amino terminus. TRPM4 encodes a Ca2+-activated nonselective cation (CAN) channel that belongs to the transient receptor potential melastatin ion channel family. Quantitative analysis of TRPM4 mRNA content in human cardiac tissue showed the highest expression level in Purkinje fibers. Cellular expression studies showed that the c.19G-->A missense mutation attenuated deSUMOylation of the TRPM4 channel. The resulting constitutive SUMOylation of the mutant TRPM4 channel impaired endocytosis and led to elevated TRPM4 channel density at the cell surface. Our data therefore revealed a gain-of-function mechanism underlying this type of familial heart block.
Figures


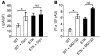

Comment in
-
Endocytic control of ion channel density as a target for cardiovascular disease.J Clin Invest. 2009 Sep;119(9):2531-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI40427. Epub 2009 Aug 24. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19726880 Free PMC article.
-
Taking a SUMO off a TRP for bad conduct.Clin Genet. 2010 Apr;77(4):328-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2009.01366_2.x. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Clin Genet. 2010. PMID: 20095982 No abstract available.
References
-
- Josephson, M.E., Zimetbaum, P., Marchlinski, F.E., and Buxton, A.E. 1998. The bradyarrhythmias: disorders of sinus node function and AV conduction disturbances. InHarrison’s principles of internal medicine . A.S. Fauci, et al., editors. McGraw-Hill. New York, New York, USA. 1253–1261.
-
- Epstein A.E., et al. ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 Guidelines for Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices): developed in collaboration with the American Association for Thoracic Surgery and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation. 2008;117:e350–e408. doi: 10.1161/CIRCUALTIONAHA.108.189742. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benson D.W. Genetics of atrioventricular conduction disease in humans. Anat. Rec. A. Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2004;280:934–939. - PubMed
-
- Brink P.A., et al. Gene for progressive familial heart block type I maps to chromosome 19q13. Circulation. 1995;91:1633–1640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

