Evaluation of the Abbott m2000rt RealTime HIV-1 assay with manual sample preparation compared with the ROCHE COBAS AmpliPrep/AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR v1.5 using specimens from East Africa
- PMID: 19729037
- PMCID: PMC2761523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.08.013
Evaluation of the Abbott m2000rt RealTime HIV-1 assay with manual sample preparation compared with the ROCHE COBAS AmpliPrep/AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR v1.5 using specimens from East Africa
Abstract
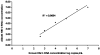
The performance of the Abbott m2000rt RealTime HIV-1 assay (RealTime HIV-1) with manual sample preparation was compared against the ROCHE COBAS AmpliPrep/AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR Test v1.5 (CAP/CA HIV-1) using samples collected from 100 donors infected with HIV and 20 donors not infected with HIV in northern Tanzania where HIV-1 subtypes A, C, D, and their recombinant forms predominate. The RealTime HIV-1 appeared to have more within-run variability at high HIV-1 RNA concentrations, but total assay variability over the dynamic range tested was within the manufacturer's claim of <0.3 SD copies/mL. Accuracy studies showed 100% concordance for positive and negative values. When continuous values were examined, CAP/CA HIV-1 yielded higher values than the RealTime HIV-1 at higher nominal HIV-1 RNA concentrations. The RealTime HIV-1 assay showed excellent linearity between 2.5 and 7.0 log copies/mL. Of negative samples, 100% showed negative results, and >95% of samples with nominal concentrations of 40 copies/mL were detected at > or = 40 copies/mL by RealTime HIV-1. Manual sample preparation may contribute to higher total assay variability. This study suggests that the Abbott m2000rt RealTime HIV-1 assay with manual sample preparation is an acceptable and feasible alternative to the conventional ROCHE COBAS AmpliPrep/AMLICOR HIV-1 Monitor v1.5 assay and that the RealTime HIV-1 assay performs well on samples from East Africa.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–10. - PubMed
-
- de Mendoza C, Koppelman M, Montes B, Ferre V, Soriano V, Cuypers H, Segondy M, Oosterlaken T. Multicenter evaluation of the NucliSens EasyQ HIV-1 v1.1 assay for the quantitative detection of HIV-1 RNA in plasma. J Virol Methods. 2005;127:54–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

