NF-kappaB-induced oxidative stress contributes to mitochondrial and cardiac dysfunction in type II diabetes
- PMID: 19729361
- PMCID: PMC2860708
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvp305
NF-kappaB-induced oxidative stress contributes to mitochondrial and cardiac dysfunction in type II diabetes
Abstract
Aims: Inflammatory molecules and their transcription factor, nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kappaB), are thought to play important roles in diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction. Here, we investigated the effects of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), a NF-kappaB inhibitor, in diabetic mice.
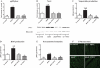
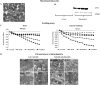
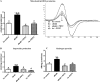
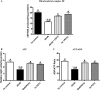
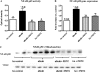
Methods and results: Obese db/db mice and heterozygous lean mice (n = 8) were allowed free access to drinking water (control) or water containing PDTC (100 mg/kg) for 20 weeks. Left ventricular (LV) function was measured using echocardiography at baseline and at study end. Mice were sacrificed and LV removed for gene expression, biochemical, immunofluorescence, and mitochondrial assays. LV and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), superoxide and peroxynitrite were measured using electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Enhanced NF-kappaB activity in db/db mice was associated with increased oxidative stress as demonstrated by increased ROS, superoxide, and peroxynitrite production, and increased NF-kappaB, gp91phox, and Nox1 expression; PDTC ameliorated these effects. Mitochondrial free radical production and structural damage were higher in the db/db group than in the control, db/db PDTC, and PDTC-treated heterozygous animal groups.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that NF-kappaB blockade with PDTC mitigates oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial structural integrity directly, through down-regulation of increased oxygen-free radicals, thereby increasing ATP synthesis and thus restoring cardiac function in type II diabetes.
Figures
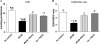
References
-
- NIDDK. Bethesda, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, NIH; 2008. National Diabetes Statistics, 2007.
-
- AHA. Metabolic Syndrome Statistics Statistical Fact Sheets. Dallas, TX: American Heart Association; 2009.
-
- Kelishadi R, Gharipour M, Sadri GH, Tavasoli AA, Amani A. Cardiovascular disease risk factors, metabolic syndrome and obesity in an Iranian population. East Mediterr Health J. 2008;14:1070–1079. - PubMed
-
- Khan KA, Sowers JR. Surgical treatment of the cardiometabolic syndrome and obesity. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2008;3:254–257. - PubMed
-
- Cai L, Kang YJ. Oxidative stress and diabetic cardiomyopathy: a brief review. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2001;1:181–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

