Association of dialysis modality and cardiovascular mortality in incident dialysis patients
- PMID: 19729428
- PMCID: PMC2758255
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01750309
Association of dialysis modality and cardiovascular mortality in incident dialysis patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: The aim of the investigation presented here was to compare the rates, causes, and timing of cardiovascular (CV) death in incident peritoneal dialysis (PD) and hemodialysis (HD) patients.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: The study included all adult Australian and New Zealand patients commencing dialysis between January 1, 1997 and December 31, 2007. Rates of and times to CV death were compared by incident rate ratios, cumulative incidence, and multivariable Cox proportional hazards model analyses. Dialysis modality was included in the model as a time-varying covariate, and a competing risks approach was used to obtain cause-specific hazard ratios.
Results: Of the 24,587 patients who commenced dialysis (first treatment PD n = 6521; HD n = 18,066) during the study, 5669 (21%) died from CV causes [PD 2044 (28%) versus HD 3625 (21%)]. The incidence rates of CV mortality in PD and HD patients were 9.99 and 7.96 per 100 patient-years, respectively (incidence rate ratio PD versus HD, 1.25; 95% confidence interval 1.12 to 1.32). PD was consistently associated with an increased hazard of CV death compared with HD after 1 yr of treatment. This increased risk in PD patients was largely accounted for by an increased risk of death due to myocardial infarction.
Conclusions: Dialysis modality is significantly associated with the risk, causes, and timing of CV death experienced by ESRD patients in Australia and New Zealand.
Figures
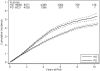

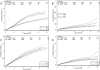
References
-
- McDonald S, Excell L: ANZDATA Registry Report 2005. Adelaide, South Australia, Australian and New Zealand Dialysis and Transplant Registry, 2006
-
- Annual Data Report Minneapolis, MN, U.S. Renal Data Systems, 2006
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ: Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 32: S112– S119, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Amin MG, Stark PC, MacLeod B, Griffith JL, Salem DN, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ: Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: A pooled analysis of community-based studies. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1307– 1315, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Keough-Ryan TM, Kiberd BA, Dipchand CS, Cox JL, Rose CL, Thompson KJ, Clase CM: Outcomes of acute coronary syndrome in a large Canadian cohort: Impact of chronic renal insufficiency, cardiac interventions, and anemia. Am J Kidney Dis 46: 845– 855, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

