Prevalence and determinants of isolated systolic hypertension among young adults: the 1999-2004 US National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey
- PMID: 19730124
- PMCID: PMC2891994
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328331b7ff
Prevalence and determinants of isolated systolic hypertension among young adults: the 1999-2004 US National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey
Abstract
Background: Little is known about isolated systolic hypertension (ISH) in younger adults. We examined the prevalence and determinants of ISH in this age group using the 1999-2004 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) and made comparisons using data from NHANES III (1988-1994).
Methods: A total of 5685 adults aged 18-39 years and not on antihypertensive medications were analyzed. Prevalence estimates of ISH and potential risk factors were estimated by age and sex. For comparison of prevalence estimates with published reports of NHANES III data, age cutoffs (18-24, 25-34, and 35-44 year) by sex were also employed. A multivariate logistic regression model tested independent determinants of ISH.
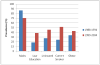
Results: ISH in young adults had a higher prevalence than systolic/diastolic hypertension (1.57 +/- 0.23% vs. 0.93 +/- 0.18%). ISH prevalence increased within the last decade particularly for men for each respective age category [men (0.8 vs. 2.2%, 1.3 vs. 2.4%, 1.3 vs. 2.4%), women (0.0 vs. 0.3%, 0.1 vs. 0.7%, 1.7 vs. 1.8%)]. On multivariate analysis, obesity [odds ratio (OR): 2.68, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.06, 6.77], male sex (OR: 2.19, 95% CI: 1.10, 4.37), education level less than high school (OR: 2.98, 95% CI: 1.10, 8.06), and current smoking (OR: 2.06, 95% CI: 1.03, 4.11) were characteristics independently associated with higher odds of ISH among young adults. Relative increases in prevalence between the surveys were noted for current smoking (24.3 vs. 51.5%), obesity (33.9 vs. 42.7%) and low educational level (18.4 vs. 38.6%).
Conclusion: ISH among young adults is increasing in prevalence, and is more common than systolic/diastolic hypertension. Obesity, smoking, and low socioeconomic status appear to be important determinants of ISH among young adults and have all increased over the last decade.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Guidelines Subcommittee 1999 World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 1999:151–83. - PubMed
-
- Franklin SS, Jacobs MJ, Wong ND, L’Italien GJ, Lapuerta P. Predominance of Isolated Systolic Hypertension Among Middle-Aged and Elderly US Hypertensives : Analysis Based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III. Hypertension. 2001;37(3):869–74. - PubMed
-
- Nichols WW, O’Rourke, Michael F, editors. McDonald’s Blood Flow In Arteries: Theoretical, Experimental And Clinical Principles. 5 ed Hodder Headline Group; London, UK: 2005.
-
- O’Rourke MF, Vlachopoulos C, Graham RM. Spurious systolic hypertension in youth. Vascular Medicine. 2000;5(3):141–5. - PubMed
-
- Haider AW, Larson MG, Franklin SS, Levy D. Systolic Blood Pressure, Diastolic Blood Pressure, and Pulse Pressure as Predictors of Risk for Congestive Heart Failure in the Framingham Heart Study. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2003;138(1):10–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

