Neuroligin-1 performs neurexin-dependent and neurexin-independent functions in synapse validation
- PMID: 19730411
- PMCID: PMC2771087
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.249
Neuroligin-1 performs neurexin-dependent and neurexin-independent functions in synapse validation
Abstract
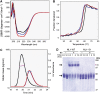
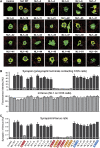
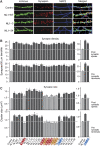
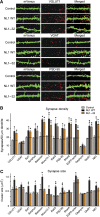
Postsynaptic neuroligins are thought to perform essential functions in synapse validation and synaptic transmission by binding to, and dimerizing, presynaptic alpha- and beta-neurexins. To test this hypothesis, we examined the functional effects of neuroligin-1 mutations that impair only alpha-neurexin binding, block both alpha- and beta-neurexin binding, or abolish neuroligin-1 dimerization. Abolishing alpha-neurexin binding abrogated neuroligin-induced generation of neuronal synapses onto transfected non-neuronal cells in the so-called artificial synapse-formation assay, even though beta-neurexin binding was retained. Thus, in this assay, neuroligin-1 induces apparent synapse formation by binding to presynaptic alpha-neurexins. In transfected neurons, however, neither alpha- nor beta-neurexin binding was essential for the ability of postsynaptic neuroligin-1 to dramatically increase synapse density, suggesting a neurexin-independent mechanism of synapse formation. Moreover, neuroligin-1 dimerization was not required for either the non-neuronal or the neuronal synapse-formation assay. Nevertheless, both alpha-neurexin binding and neuroligin-1 dimerization were essential for the increase in apparent synapse size that is induced by neuroligin-1 in transfected neurons. Thus, neuroligin-1 performs diverse synaptic functions by mechanisms that include as essential components of alpha-neurexin binding and neuroligin dimerization, but extend beyond these activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A splice code for trans-synaptic cell adhesion mediated by binding of neuroligin 1 to alpha- and beta-neurexins.Neuron. 2005 Oct 20;48(2):229-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.08.026. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 16242404
-
Direct visualization of trans-synaptic neurexin-neuroligin interactions during synapse formation.J Neurosci. 2014 Nov 5;34(45):15083-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0348-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25378172 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection of synapse induction by neuroligins: effect of a neuroligin mutation associated with autism.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 10;280(23):22365-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410723200. Epub 2005 Mar 29. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15797875
-
A matter of balance: role of neurexin and neuroligin at the synapse.Neurochem Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):1174-89. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1029-9. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23559421 Review.
-
Neurexin-neuroligin signaling in synapse development.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Feb;17(1):43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.01.011. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17275284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative splicing at neuroligin site A regulates glycan interaction and synaptogenic activity.Elife. 2020 Sep 11;9:e58668. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58668. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32915137 Free PMC article.
-
Autism-linked neuroligin-3 R451C mutation differentially alters hippocampal and cortical synaptic function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 16;108(33):13764-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111093108. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21808020 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroligins Sculpt Cerebellar Purkinje-Cell Circuits by Differential Control of Distinct Classes of Synapses.Neuron. 2015 Aug 19;87(4):781-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.020. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 26291161 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroligin 1 regulates spines and synaptic plasticity via LIMK1/cofilin-mediated actin reorganization.J Cell Biol. 2016 Feb 15;212(4):449-63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201509023. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26880202 Free PMC article.
-
Functional dependence of neuroligin on a new non-PDZ intracellular domain.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Jun;14(6):718-26. doi: 10.1038/nn.2825. Epub 2011 May 1. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21532576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arac D, Boucard AA, Ozkan E, Strop P, Newell E, Südhof TC, Brunger AT (2007) Structures of neuroligin-1 and the neuroligin-1/neurexin-1beta complex reveal specific protein-protein and protein-Ca2+ interactions. Neuron 56: 992–1003 - PubMed
-
- Biederer T, Sara Y, Mozhayeva M, Atasoy D, Liu X, Kavalali ET, Südhof TC (2002) SynCAM, a synaptic adhesion molecule that drives synapse assembly. Science 297: 1525–1531 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

