The availability and use of out-of-hospital physiologic information to identify high-risk injured children in a multisite, population-based cohort
- PMID: 19731152
- PMCID: PMC3008574
- DOI: 10.1080/10903120903144882
The availability and use of out-of-hospital physiologic information to identify high-risk injured children in a multisite, population-based cohort
Abstract
Objective: The validity of using adult physiologic criteria to triage injured children in the out-of-hospital setting remains unproven. Among children meeting adult field physiologic criteria, we assessed the availability of physiologic information, the incidence of death or prolonged hospitalization, and whether age-specific criteria would improve the specificity of the physiologic triage step.
Methods: We analyzed a prospective, out-of-hospital cohort of injured children aged < or =14 years collected from December 2005 through February 2007 by 237 emergency medical services (EMS) agencies transporting to 207 acute care hospitals (trauma and nontrauma centers) in 11 sites across the United States and Canada. Inclusion criteria were standard adult physiologic values: systolic blood pressure (SBP) < or =90 mmHg, respiratory rate < 10 or > 29 breaths/min, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score < or =12, and field intubation attempt. Seven physiologic variables (including age-specific values) and three demographic and mechanism variables were included in the analysis. "High-risk" children included those who died (field or in-hospital) or were hospitalized > 2 days. The decision tree was derived and validated using binary recursive partitioning.
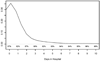
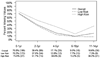
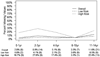
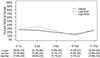
Results: Nine hundred fifty-five children were included in the analysis, of whom 62 (6.5%) died and 117 (12.3%) were hospitalized > 2 days. Missing values were common, ranging from 6% (respiratory rate) to 53% (pulse oximetry), and were associated with younger age and high-risk outcome. The final decision rule included four variables (assisted ventilation, GCS score < 11, pulse oximetry < 95%, and SBP > 96 mmHg), which demonstrated improved specificity (71.7% [95% confidence interval (CI) 66.7-76.6%]) at the expense of missing high-risk children (sensitivity 76.5% [95% CI 66.4-86.6%]).
Conclusions: The incidence of high-risk injured children meeting adult physiologic criteria is relatively low and the findings from this sample do not support using age-specific values to better identify such children. However, the amount and pattern of missing data may compromise the value and practical use of field physiologic information in pediatric triage.
Figures

References
-
- Cooper A, Barlow B, DiScala C, String D, Ray K, Mottley L. Efficacy of pediatric trauma care: results of a population-based study. J Pediatr Surg. 1993;28:299–303. - PubMed
-
- Hulka F, Mullins RJ, Mann NC, et al. Influence of a statewide trauma system on pediatric hospitalization and outcome. J Trauma. 1997;42:514–519. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DL, Krishnamurthy S. Send severely head-injured children to a pediatric trauma center. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1996;25:309–314. - PubMed
-
- Hall JR, Reyes HM, Meller JL, Loeff DS, Dembek R. The outcome for children with blunt trauma is best at a pediatric trauma center. J Pediatr Surg. 1996;31:72–77. - PubMed
-
- Pracht EE, Tepas JJ, Langland-Orban B, Simpson L, Pieper P, Flint LM. Do pediatric patients with trauma in Florida have reduced mortality rates when treated in designated trauma centers? J Pediatr Surg. 2008;43:212–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HL077866/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01 HL077863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077881/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077873/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077872/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077881/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077908/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077877/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077908/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077872/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077866/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077873/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
