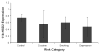Fetal effects of psychoactive drugs
- PMID: 19732616
- PMCID: PMC2767264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2009.06.002
Fetal effects of psychoactive drugs
Abstract
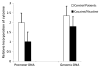
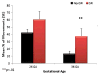
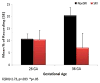
Psychoactive drug use by pregnant women has the potential to effect fetal development; the effects are often thought to be drug-specific and gestational age dependent. This article describes the effects of three drugs with similar molecular targets that involve monoaminergic transmitter systems: cocaine, methamphetamine, and selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) used to treat maternal depression during pregnancy. We propose a possible common epigenetic mechanism for their potential effects on the developing child. We suggest that exposure to these substances acts as a stressor that affects fetal programming, disrupts fetal placental monoamine transporter expression and alters neuroendocrine and neurotransmitter system development. We also discuss neurobehavioral techniques that may be useful in the early detection of the effects of in utero drug exposure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluoxetine during pregnancy: impact on fetal development.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2005;17(6):641-50. doi: 10.1071/rd05030. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2005. PMID: 16263070 Review.
-
[Use of SSRIs during pregnancy and possible consequences for the development of the child].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2007 Dec 29;151(52):2873-4. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2007. PMID: 18257430 Dutch.
-
[The Medical Products Agency about SSRI to pregnant women and adverse effects on the fetus. Long-term adverse effects are not proved, documentation is insufficient, more research is necessary].Lakartidningen. 2005 Mar 7-13;102(10):791-2; author reply 792. Lakartidningen. 2005. PMID: 15839178 Swedish. No abstract available.
-
Findings from selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor-exposed neonates should be interpreted with caution.Pediatrics. 2004 Dec;114(6):1739-40; author reply 1740-1. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1626. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15574649 No abstract available.
-
[Treatment of depressed pregnant women by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: risk for the foetus and the newborn].Encephale. 2010 Jun;36 Suppl 2:D133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2009.06.005. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Encephale. 2010. PMID: 20513456 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Effects of prenatal methamphetamine exposure: a review of cognitive and neuroimaging studies.Metab Brain Dis. 2014 Jun;29(2):245-54. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9470-7. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Metab Brain Dis. 2014. PMID: 24370774 Review.
-
The Adverse Effects of Prenatal METH Exposure on the Offspring: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 14;12:715176. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.715176. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34335277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal methamphetamine exposure and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children from 1 to 3 years.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2014 Mar-Apr;42:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2014. PMID: 24566524 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal methamphetamine exposure is associated with reduced subcortical volumes in neonates.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2018 Jan-Feb;65:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 22. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2018. PMID: 29069607 Free PMC article.
-
Subcortical and cortical structural central nervous system changes and attention processing deficits in preschool-aged children with prenatal methamphetamine and tobacco exposure.Dev Neurosci. 2012;34(4):327-41. doi: 10.1159/000341119. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Dev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22907274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson JG. Current status of teratology: General principles and mechanisms derived from animal studies. In: Wilson JG, Fraser FC, editors. Handbook of Teratology, General Principles and Etiology. Vol. 1. New York: Plenum Press; 1977. pp. 47–74.
-
- Wisner KL, Zarin DA, Holmboe ES, et al. Risk-benefit decision making for treatment of depression during pregnancy. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157(12):1933–1940. - PubMed
-
- Yonkers KA, Wisner KL, Stowe Z, et al. Management of bipolar disorder during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Am J Psychiatry. 2004 Apr;161(4):608–620. - PubMed
-
- Lester B, Kosofsky B. Neurobiology of Mental Illness. In: Charney D, Nestler E, editors. Effects of Drugs of Abuse on Brain Development. London: Oxford University Press; 2009. pp. 801–827.
-
- Bertalanffy Lv. General Systems Theory. New York: Brazilier; 1968.