Removal of bound Triton X-100 from purified bovine heart cytochrome bc1
- PMID: 19733142
- PMCID: PMC2760635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2009.08.042
Removal of bound Triton X-100 from purified bovine heart cytochrome bc1
Abstract
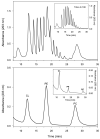
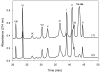
Cytochrome bc(1) isolated from Triton X-100-solubilized mitochondrial membranes contains up to 120 nmol of Triton X-100 bound per nanomole of the enzyme. Purified cytochrome bc(1) is fully active; however, protein-bound Triton X-100 significantly interferes with structural studies of the enzyme. Removal of Triton X-100 bound to bovine cytochrome bc(1) was accomplished by incubation with Bio-Beads SM-2 in the presence of sodium cholate. Sodium cholate is critical because it does not interfere with the adsorption of protein on the hydrophobic surface of the beads. The resulting Triton X-100-free cytochrome bc(1) retained nearly full activity, absorption spectra, subunit, and phospholipid composition.
Figures
References
-
- Robinson NC, Wiginton D, Talbert L. Phenyl-Sepharose-mediated detergent-exchange chromatography: its application to exchange of detergents bound to membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1984;23:6121–6126. - PubMed
-
- Gomez B, Jr., Robinson NC. Phospholipase digestion of bound cardiolipin reversibly inactivates bovine cytochrome bc1. Biochemistry. 1999;38:9031–9038. - PubMed
-
- Seddon AM, Curnow P, Booth PJ. Membrane proteins, lipids and detergents: not just a soap opera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1666:105–117. - PubMed
-
- Holloway PW. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal. Biochem. 1973;53:304–308. - PubMed
-
- Furth AJ. Removing unbound detergent from hydrophobic proteins. Anal. Biochem. 1980;109:207–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

