Potential vascular actions of 2-methoxyestradiol
- PMID: 19734053
- PMCID: PMC2761235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.04.007
Potential vascular actions of 2-methoxyestradiol
Abstract
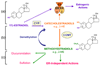
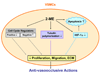
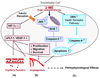
2-Methoxyestradiol (2-ME) is a biologically active metabolite of 17beta-estradiol that appears to inhibit key processes associated with cell replication in vitro. The molecule has been suggested to have potent growth-inhibitory effects on proliferating cells, including smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells, and may be antiangiogenic. Because of these potential roles for 2-ME, its lack of cytotoxicity and low estrogenic activity, we hypothesize that 2-ME could be a valuable therapeutic molecule for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Whether 2-ME is as effective in vivo as it is in vitro at modulating vascular processes remains controversial. Here we discuss recent developments regarding mechanisms by which 2-ME might regulate vascular activity and angiogenesis and speculate on the therapeutic implications of these developments.
Figures

References
-
- Zhu BT, Conney AH. Is 2-methoxyestradiol an endogenous estrogen metabolite that inhibits mammary carcinogenesis? Cancer Research. 1998;58:2269–2277. - PubMed
-
- Dubey RK, et al. Cardiovascular pharmacology of estradiol metabolites. Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics. 2004;308:403–409. - PubMed
-
- Lakhani NJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and drug metabolism - Characterization of in vitro and in vivo metabolic pathways of the investigational anticancer agent, 2-methoxyestradiol. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2007;96:1821–1831. - PubMed
-
- Dubey RK, et al. 2-Methoxyestradiol: A potential treatment for multiple proliferative disorders. Endocrinology. 2007;148:4125–4127. - PubMed
-
- Ho A, et al. SAR studies of 2-methoxyestradiol and development of its analogs as probes of anti-tumor mechanisms. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2006;16:3383–3387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

