A UV-responsive internal ribosome entry site enhances serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 expression for DNA damage repair
- PMID: 19734144
- PMCID: PMC2781509
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.015800
A UV-responsive internal ribosome entry site enhances serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 expression for DNA damage repair
Abstract
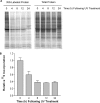
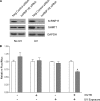
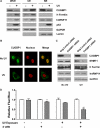
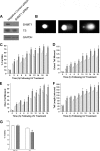
Thymidine nucleotides are required for faithful DNA synthesis and repair, and their de novo biosynthesis is regulated by serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (SHMT1). The SHMT1 transcript contains a heavy chain ferritin, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H2, and CUG-binding protein 1-responsive internal ribosome entry site (IRES) that regulates SHMT1 translation. In this study a non-lethal dose of UVC is shown to increase SHMT1 IRES activity and protein levels in four different cell lines. The mechanism for the UV-induced activation of the SHMT1 IRES involves an increase in heavy chain ferritin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H2 expression and the translocation of CUG-binding protein 1 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. The UV-induced increase in SHMT1 translation is accompanied by an increase in the small ubiquitin-like modifier-dependent nuclear localization of the de novo thymidylate biosynthesis pathway and a decrease in DNA strand breaks, indicating a role for SHMT1 and nuclear folate metabolism in DNA repair.
Figures






References
-
- Ravanat J. L., Douki T., Cadet J. (2001) J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 63, 88–102 - PubMed
-
- Tornaletti S., Hanawalt P. C. (1999) Biochimie 81, 139–146 - PubMed
-
- de Laat W. L., Jaspers N. G., Hoeijmakers J. H. (1999) Genes Dev. 13, 768–785 - PubMed
-
- Hori T., Ayusawa D., Shimizu K., Koyama H., Seno T. (1984) Cancer Res. 44, 703–709 - PubMed
-
- Scott J. M., Weir D. G. (1981) Lancet 2, 337–340 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

