An interactive regulatory network controls stress response in Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003
- PMID: 19734308
- PMCID: PMC2772463
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00897-09
An interactive regulatory network controls stress response in Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003
Abstract
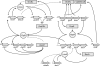
Members of the genus Bifidobacterium are gram-positive bacteria that commonly are found in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of mammals, including humans. Because of their perceived probiotic properties, they frequently are incorporated as functional ingredients in food products. From probiotic production to storage and GIT delivery, bifidobacteria encounter a plethora of stresses. To cope with these environmental challenges, they need to protect themselves through stress-induced adaptive responses. We have determined the response of B. breve UCC2003 to various stresses (heat, osmotic, and solvent) using transcriptome analysis, DNA-protein interactions, and GusA reporter fusions, and we combined these with results from an in silico analysis. The integration of these results allowed the formulation of a model for an interacting regulatory network for stress response in B. breve UCC2003 where HspR controls the SOS response and the ClgR regulon, which in turn regulates and is regulated by HrcA. This model of an interacting regulatory network is believed to represent the paradigm for stress adaptation in bifidobacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Andersen, M. T., L. Brondsted, B. M. Pearson, F. Mulholland, M. Parker, C. Pin, J. M. Wells, and H. Ingmer. 2005. Diverse roles for HspR in Campylobacter jejuni revealed by the proteome, transcriptome and phenotypic characterization of an hspR mutant. Microbiology 151:905-915. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, T. L., and C. Elkan. 1995. The value of prior knowledge in discovering motifs with MEME. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 3:21-29. - PubMed
-
- Bellier, A., M. Gominet, and P. Mazodier. 2006. Post-translational control of the Streptomyces lividans ClgR regulon by ClpP. Microbiology 152:1021-1027. - PubMed
-
- Bi, C., and C. J. Benham. 2004. WebSIDD: server for predicting stress-induced duplex destabilized (SIDD) sites in superhelical DNA. Bioinformatics 20:1477-1479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

