An integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-c-Src oncogenic unit promotes anchorage-independence and tumor progression
- PMID: 19734908
- PMCID: PMC2759406
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2009
An integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-c-Src oncogenic unit promotes anchorage-independence and tumor progression
Abstract
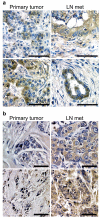
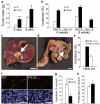
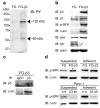
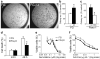
Integrins regulate adhesion-dependent growth, survival and invasion of tumor cells. In particular, expression of integrin alpha(v)beta(3) is associated with progression of a variety of human tumors. Here we reveal a previously undescribed adhesion-independent role for integrin alpha(v)beta(3) in pancreatic cancer and other carcinomas. Specifically, alpha(v)beta(3) expressed in carcinoma cells enhanced anchorage-independent tumor growth in vitro and increased lymph node metastases in vivo. These effects required recruitment of c-Src to the beta(3) integrin cytoplasmic tail, leading to c-Src activation, Crk-associated substrate (CAS) phosphorylation and tumor cell survival that, unexpectedly, was independent of cell adhesion or focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation. Pharmacological blockade of c-Src kinase activity or decreased expression of endogenous alpha(v)beta(3) integrin or c-Src not only inhibited anchorage-independent growth but also suppressed metastasis in vivo, yet these manipulations did not affect tumor cell migration or invasion. These data define an unexpected role for an integrin as a mediator of anchorage independence, suggesting that an alpha(v)beta(3)-c-Src signaling module may account for the aggressive behavior of integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-expressing tumors in humans.
Figures

References
-
- Guo W, Giancotti FG. Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:816–826. - PubMed
-
- Schlaepfer DD, Mitra SK, Ilic D. Control of motile and invasive cell phenotypes by focal adhesion kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1692:77–102. - PubMed
-
- Roberts WG, et al. Antitumor activity and pharmacology of a selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, PF-562,271. Cancer research. 2008;68:1935–1944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA121938/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA050286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA129660/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA045726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA123774/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA123774/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA129660/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA95262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA078045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL57900/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057900/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA78045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

