Endoglin phosphorylation by ALK2 contributes to the regulation of prostate cancer cell migration
- PMID: 19736306
- PMCID: PMC2832542
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgp217
Endoglin phosphorylation by ALK2 contributes to the regulation of prostate cancer cell migration
Abstract
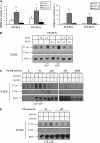
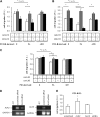
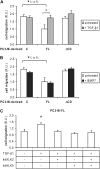
Endoglin, a transmembrane glycoprotein that acts as a transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) coreceptor, is downregulated in PC3-M metastatic prostate cancer cells. When restored, endoglin expression in PC3-M cells inhibits cell migration in vitro and attenuates the tumorigenicity of PC3-M cells in SCID mice, though the mechanism of endoglin regulation of migration in prostate cancer cells is not known. The current study indicates that endoglin is phosphorylated on cytosolic domain threonine residues by the TGF-beta type I receptors ALK2 and ALK5 in prostate cancer cells. Importantly, in the presence of constitutively active ALK2, endoglin did not inhibit cell migration, suggesting that endoglin phosphorylation regulated PC3-M cell migration. Therefore, our results suggest that endoglin phosphorylation is a mechanism with relevant functional consequences in prostate cancer cells. These data demonstrate for the first time that TGF-beta receptor-mediated phosphorylation of endoglin is a Smad-independent mechanism involved in the regulation of prostate cancer cell migration.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Endoglin inhibits prostate cancer motility via activation of the ALK2-Smad1 pathway.Oncogene. 2007 Nov 8;26(51):7240-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210533. Epub 2007 May 14. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17496924 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of transforming growth factor β1 in malignant prostate cells is partly caused by a runaway of TGF-β1 auto-induction mediated through a defective recruitment of protein phosphatase 2A by TGF-β type I receptor.Urology. 2010 Dec;76(6):1519.e8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2010.03.061. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Urology. 2010. PMID: 21030067 Free PMC article.
-
ALK5 phosphorylation of the endoglin cytoplasmic domain regulates Smad1/5/8 signaling and endothelial cell migration.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Mar;31(3):435-41. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp327. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20042635 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, a vascular dysplasia affecting the TGF-beta signaling pathway.Clin Med Res. 2006 Mar;4(1):66-78. doi: 10.3121/cmr.4.1.66. Clin Med Res. 2006. PMID: 16595794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the TGF-β coreceptor endoglin in cancer.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Dec 14;10:2367-84. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.230. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 21170488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoglin in the Spotlight to Treat Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 20;22(6):3186. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063186. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoglin as a predictive biomarker for pemetrexed sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer: a cellular study.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 10;95(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s00280-024-04734-9. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39792181
-
ACVR1 Function in Health and Disease.Cells. 2019 Oct 31;8(11):1366. doi: 10.3390/cells8111366. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31683698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostate cancer: the need for biomarkers and new therapeutic targets.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014 Jan;15(1):16-42. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1300106. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014. PMID: 24390742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Janus Kinase 1 synergizes docetaxel sensitivity in prostate cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(17):8187-8200. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16684. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34322995 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

