Vitamin D and respiratory health
- PMID: 19737226
- PMCID: PMC2759054
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04001.x
Vitamin D and respiratory health
Abstract
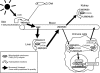
Vitamin D is now known to be of physiological importance outside of bone health and calcium homeostasis, and there is mounting evidence that it plays a beneficial role in the prevention and/or treatment of a wide range of diseases. In this brief review the known effects of vitamin D on immune function are described in relation to respiratory health. Vitamin D appears capable of inhibiting pulmonary inflammatory responses while enhancing innate defence mechanisms against respiratory pathogens. Population-based studies showing an association between circulating vitamin D levels and lung function provide strong justification for randomized controlled clinical trials of vitamin D supplementation in patients with respiratory diseases to assess both efficacy and optimal dosage.
Figures
References
-
- Etten EV, Mathieu C. Immunoregulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: basic concepts. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;97:93–101. - PubMed
-
- Ebert R, Schütze N, Adamski J, Jakob F. Vitamin D signaling is modulated on multiple levels in health and disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006;248:149–59. - PubMed
-
- Laaksi I, Ruohola J-P, Tuohimaa P, et al. An association of serum vitamin D concentrations < 40 nmol/L with acute respiratory tract infection in young Finnish men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:714–17. - PubMed
-
- Baeke F, Ev E, Gysemans C, Overbergh L, Mathieu C. Vitamin D signaling in immune-mediated disorders: evolving insights and therapeutic opportunities. Mol Aspects Med. 2008;29:376–87. - PubMed
-
- Holick MF, Chen TC. Vitamin D deficiency: a worldwide problem with health consequences. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:1080S–6S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

