The protein kinase IKKepsilon regulates energy balance in obese mice
- PMID: 19737522
- PMCID: PMC2756060
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.046
The protein kinase IKKepsilon regulates energy balance in obese mice
Abstract
Obesity is associated with chronic low-grade inflammation that negatively impacts insulin sensitivity. Here, we show that high-fat diet can increase NF-kappaB activation in mice, which leads to a sustained elevation in level of IkappaB kinase epsilon (IKKepsilon) in liver, adipocytes, and adipose tissue macrophages. IKKepsilon knockout mice are protected from high-fat diet-induced obesity, chronic inflammation in liver and fat, hepatic steatosis, and whole-body insulin resistance. These mice show increased energy expenditure and thermogenesis via enhanced expression of the uncoupling protein UCP1. They maintain insulin sensitivity in liver and fat, without activation of the proinflammatory JNK pathway. Gene expression analyses indicate that IKKepsilon knockout reduces expression of inflammatory cytokines, and changes expression of certain regulatory proteins and enzymes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. Thus, IKKepsilon may represent an attractive therapeutic target for obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and other complications associated with these disorders.
Figures
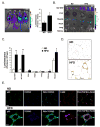


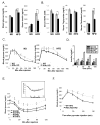


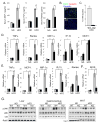
Comment in
-
IKKepsilon: a bridge between obesity and inflammation.Cell. 2009 Sep 4;138(5):834-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.018. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19737512
-
IkappaB kinase epsilon: a potential therapeutic target for obesity (and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease)?Hepatology. 2010 Jan;51(1):336-8. doi: 10.1002/hep.23459. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20034032 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Poli G, Olefsky J, Karin M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2005;11:191–198. - PubMed
-
- Armoni M, Harel C, Karni S, Chen H, Bar-Yoseph F, Ver MR, Quon MJ, Karnieli E. FOXO1 represses peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma1 and -gamma2 gene promoters in primary adipocytes. A novel paradigm to increase insulin sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:19881–19891. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury MW. Lipid metabolism and liver inflammation. I. Hepatic fatty acid uptake: possible role in steatosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G194–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

