The F-BAR domain of srGAP2 induces membrane protrusions required for neuronal migration and morphogenesis
- PMID: 19737524
- PMCID: PMC2797480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.047
The F-BAR domain of srGAP2 induces membrane protrusions required for neuronal migration and morphogenesis
Abstract
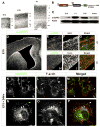
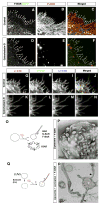
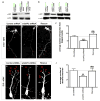
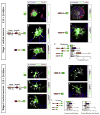
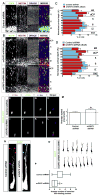
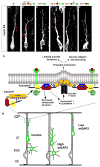
During brain development, proper neuronal migration and morphogenesis is critical for the establishment of functional neural circuits. Here we report that srGAP2 negatively regulates neuronal migration and induces neurite outgrowth and branching through the ability of its F-BAR domain to induce filopodia-like membrane protrusions resembling those induced by I-BAR domains in vivo and in vitro. Previous work has suggested that in nonneuronal cells filopodia dynamics decrease the rate of cell migration and the persistence of leading edge protrusions. srGAP2 knockdown reduces leading process branching and increases the rate of neuronal migration in vivo. Overexpression of srGAP2 or its F-BAR domain has the opposite effects, increasing leading process branching and decreasing migration. These results suggest that F-BAR domains are functionally diverse and highlight the functional importance of proteins directly regulating membrane deformation for proper neuronal migration and morphogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Aspenstrom P, Fransson A, Richnau N. Pombe Cdc15 homology proteins: regulators of membrane dynamics and the actin cytoskeleton. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:670–679. - PubMed
-
- Ayala R, Shu T, Tsai LH. Trekking across the brain: the journey of neuronal migration. Cell. 2007;128:29–43. - PubMed
-
- Bacon C, Endris V, Rappold G. Dynamic expression of the Slit-Robo GTPase activating protein genes during development of the murine nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 2009;513:224–236. - PubMed
-
- Bear JE, Loureiro JJ, Libova I, Fassler R, Wehland J, Gertler FB. Negative regulation of fibroblast motility by Ena/VASP proteins. Cell. 2000;101:717–728. - PubMed
-
- Bear JE, Svitkina TM, Krause M, Schafer DA, Loureiro JJ, Strasser GA, Maly IV, Chaga OY, Cooper JA, Borisy GG, et al. Antagonism between Ena/VASP proteins and actin filament capping regulates fibroblast motility. Cell. 2002;109:509–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

