Optic disc morphology in open-angle glaucoma compared with anterior ischemic optic neuropathies
- PMID: 19737875
- PMCID: PMC2868394
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-3492
Optic disc morphology in open-angle glaucoma compared with anterior ischemic optic neuropathies
Abstract
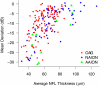
Purpose. To compare optic disc topography performed by confocal laser ophthalmoscopy in eyes with nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AAION), and open-angle glaucoma (OAG), adjusting for the amount of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) loss, as measured by nerve fiber layer (NFL) thickness and average visual field loss. Methods. At four referral centers, patients who met specific diagnostic criteria for OAG (103 persons, 152 eyes), NAION (53 persons, 57 eyes), or AAION (18 persons, 20 eyes) underwent Heidelberg Retinal Tomography (HRT; Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany), Stratus Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT; Carl Zeiss Meditec, Inc., Dublin, CA), and Humphrey visual field testing (HFA; Carl Zeiss Meditec, Inc.). HRT parameters were compared in univariate and multivariate models, accounting for degree of RGC loss by either OCT NFL thickness or visual field mean deviation (MD). Acute AION occurred at least 6 weeks before testing. Results. After adjustment for degree of injury according to either MD or mean NFL thickness, all HRT parameters were significantly different between OAG and both NAION and AAION. With similar damage, OAG eyes had larger, deeper cups; smaller rims; more cup volume; and less rim volume (all P < or = 0.001). There were differences in disc topography between NAION and AAION, but they were not consistent for both measures of damage. Disc area and MD were also significantly associated with many HRT parameters. NFL thickness was greater at the same MD for both AAION and NAION compared with OAG. Conclusions. NAION and AAION cause loss of RGCs, but have significantly different disc topography compared with OAG at a given level of RGC loss.
Figures

Comment in
-
Linear relation between structure and function.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Dec;51(12):6891; author reply 6891-2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4628. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 21123774 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hayreh SS, Jonas JB. Optic disc morphology after arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology 2001;108:1586–1594 - PubMed
-
- Sebag J, Thomas JV, Epstein DL, Grant WM. Optic disc cupping in arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy resembles glaucomatous cupping. Ophthalmology 1986;93:357–361 - PubMed
-
- Danesh-Meyer HV, Savino PJ, Sergott RC. The prevalence of cupping in end-stage arteritic and nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology 2001;108:593–598 - PubMed
-
- Quigley HA, Anderson DR. Cupping of the optic disc in ischemic optic neuropathy. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1977;83:755–762 - PubMed
-
- Danesh-Meyer H, Savino PJ, Spaeth GL, Gamble GD. Comparison of arteritic and nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathies with the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph. Ophthalmology 2005;112:1104–1112 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

