BCL9 promotes tumor progression by conferring enhanced proliferative, metastatic, and angiogenic properties to cancer cells
- PMID: 19738061
- PMCID: PMC4321734
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0773
BCL9 promotes tumor progression by conferring enhanced proliferative, metastatic, and angiogenic properties to cancer cells
Abstract
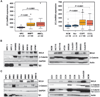
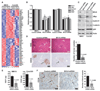
Several components of the Wnt signaling cascade have been shown to function either as tumor suppressor proteins or as oncogenes in multiple human cancers, underscoring the relevance of this pathway in oncogenesis and the need for further investigation of Wnt signaling components as potential targets for cancer therapy. Here, using expression profiling analysis as well as in vitro and in vivo functional studies, we show that the Wnt pathway component BCL9 is a novel oncogene that is aberrantly expressed in human multiple myeloma as well as colon carcinoma. We show that BCL9 enhances beta-catenin-mediated transcriptional activity regardless of the mutational status of the Wnt signaling components and increases cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and the metastatic potential of tumor cells by promoting loss of epithelial and gain of mesenchymal-like phenotype. Most importantly, BCL9 knockdown significantly increased the survival of xenograft mouse models of cancer by reducing tumor load, metastasis, and host angiogenesis through down-regulation of c-Myc, cyclin D1, CD44, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression by tumor cells. Together, these findings suggest that deregulation of BCL9 is an important contributing factor to tumor progression. The pleiotropic roles of BCL9 reported in this study underscore its value as a drug target for therapeutic intervention in several malignancies associated with aberrant Wnt signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Targeted disruption of the BCL9/β-catenin complex inhibits oncogenic Wnt signaling.Sci Transl Med. 2012 Aug 22;4(148):148ra117. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003808. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22914623 Free PMC article.
-
miR-30-5p functions as a tumor suppressor and novel therapeutic tool by targeting the oncogenic Wnt/β-catenin/BCL9 pathway.Cancer Res. 2014 Mar 15;74(6):1801-13. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3311-T. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24599134 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by regulating the expression of BCL9 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 11;7:40446. doi: 10.1038/srep40446. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28074862 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between microRNA30a/b/c/d/e-5p and the canonical Wnt pathway: implications for multiple myeloma therapy.Cancer Res. 2014 Oct 1;74(19):5351-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0994. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25228654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Wnt-dependent and Wnt-independent functions of BCL9 in development, tumorigenesis, and immunity: Implications in therapeutic opportunities.Genes Dis. 2023 Apr 11;11(2):701-710. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.012. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Cyclophilin A-CD147 complex promotes the proliferation and homing of multiple myeloma cells.Nat Med. 2015 Jun;21(6):572-80. doi: 10.1038/nm.3867. Epub 2015 May 25. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26005854 Free PMC article.
-
FOXP1 potentiates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Sci Signal. 2015 Feb 3;8(362):ra12. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005654. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 25650440 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of predictive biomarkers for postoperative recurrence of stage II/III colorectal cancer using genomic sequencing.Cancer Med. 2022 Sep;11(18):3457-3470. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4710. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35343095 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Myeloma With Amplification of Chr1q: Therapeutic Opportunity and Challenges.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 14;12:961421. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.961421. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35912171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sonic hedgehog acts as a negative regulator of {beta}-catenin signaling in the adult tongue epithelium.Am J Pathol. 2010 Jul;177(1):404-14. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091079. Epub 2010 May 27. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20508033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810. - PubMed
-
- Staal FJ, Clevers HC. WNT signalling and haematopoiesis: a WNT-WNT situation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Polakis P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1837–1851. - PubMed
-
- He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, et al. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science. 1998;281:1509–1512. - PubMed
-
- Tetsu O, McCormick F. β-Catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature. 1999;398:422–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

