Mitochondrial ROS and radiation induced transformation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- PMID: 19738419
- PMCID: PMC2795790
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.8.20.9648
Mitochondrial ROS and radiation induced transformation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts
Abstract
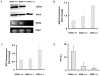
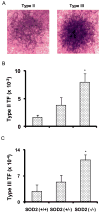
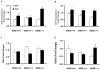
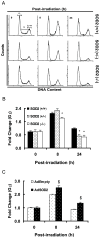
Manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2) is a nuclear encoded and mitochondria localized antioxidant enzyme that converts mitochondria derived superoxide to hydrogen peroxide. This study investigates the hypothesis that mitochondria derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulate ionizing radiation (IR) induced transformation in normal cells. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) with wild type SOD2 (+/+), heterozygous SOD2 (+/-), and homozygous SOD2 (-/-) genotypes were irradiated with equitoxic doses of IR, and assayed for transformation frequency, cellular redox environment, DNA damage, and cell cycle checkpoint activation. Transformation frequency increased ( approximately 5-fold) in SOD2 (-/-) compared to SOD2 (+/+) MEFs. Cellular redox environment (GSH, GSSG, DHE and DCFH-oxidation) did not show any significant change within 24 h post-IR. However, a significant increase in cellular ROS levels was observed at 72 h post-IR in SOD2 (-/-) compared to SOD2 (+/+) MEFs, which was consistent with an increase in GSSG in SOD2 (-/-) MEFs. Late ROS accumulation was associated with an increase in micronuclei frequency in SOD2 (-/-) MEFs. Exit from G(2) was accelerated in irradiated SOD2 (+/-) and SOD2 (-/-) compared to SOD2 (+/+) MEFs. These results support the hypothesis that SOD2 activity and mitochondria generated ROS regulate IR induced transformation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Preventing Dr. Jekyll from becoming Mr. Hyde: is manganese superoxide dismutase the key to prevent radiation-induced neoplastic transformation?Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Oct;8(20):1972-3. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.20.9941. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19823029 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hall EJ. Radiobiology for the radiologist. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2000.
-
- Biaglow JE, Mitchell JB, Held K. The importance of peroxide and superoxide in the X-ray response. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;22:665–9. - PubMed
-
- Oberley LW, Lindgren LA, Baker SA, Stevens RH. Superoxide lon as the cause of the oxygen effect. Radiat Res. 1976;68:320–8. - PubMed
-
- Biaglow JE, Clark EP, Epp ER, Morse GM, Varnes ME, Mitchell JB. Nonprotein thiols and the radiation response of A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1983;44:489–95. - PubMed
-
- Epperly MW, Epstein CJ, Travis EL, Greenberger JS. Decreased pulmonary radiation resistance of manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD)-deficient mice is corrected by human manganese superoxide dismutase-Plasmid/Liposome (SOD2-PL) intratracheal gene therapy. Radiat Res. 2000;154:365–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
