Elevation of interleukin-18 in chronic hepatitis C: implications for hepatitis C virus pathogenesis
- PMID: 19740312
- PMCID: PMC2753952
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03021.x
Elevation of interleukin-18 in chronic hepatitis C: implications for hepatitis C virus pathogenesis
Abstract
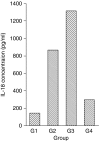
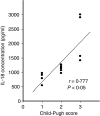
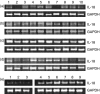
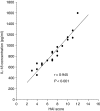
The outcome of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is determined by the interplay between the virus and the host immune response. Interleukin (IL)-18, an interferon-gamma-inducing factor, plays a critical role in the T helper type 1 (Th1) response required for host defence against viruses, and antibodies to IL-18 have been found to prevent liver damage in a murine model. The present study was conducted to investigate the possible role of IL-18 in the pathogenesis and persistence of HCV. IL-18 levels were measured in sera of 50 patients at various stages of HCV infection (resolved, chronic and cirrhosis) and compared with those of normal controls. IL-18 gene expression was studied in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from each group, and in liver biopsy tissue from patients with chronic hepatitis C. The mean levels of IL-18 in sera were markedly elevated in patients with chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis, and were reduced in patients with resolved HCV infection. The serum IL-18 concentrations were related to the Child-Pugh severity of liver disease in cirrhotic patients. There also existed a strong positive correlation of IL-18 levels with histological activity score and necrosis. IL-18 mRNA expression was significantly up-regulated in the PBMC of cirrhotic patients when compared with other groups, while in the liver, higher levels of IL-18 transcripts were expressed in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The results of our study indicate that IL-18 levels reflect the severity and activity of HCV infection, and may contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of liver disease associated with HCV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokine mRNA expression in hepatitis C virus infection: TH1 predominance in patients with chronic hepatitis C and TH1-TH2 cytokine profile in subjects with self-limited disease.J Viral Hepat. 2008 Feb;15(2):145-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2007.00908.x. J Viral Hepat. 2008. PMID: 18184198
-
Th1 and Th2 cytokine profiles induced by hepatitis C virus F protein in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from chronic hepatitis C patients.Immunol Lett. 2013 May;152(2):89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 13. Immunol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23680070
-
Pathological Roles of Interleukin-22 in the Development of Recurrent Hepatitis C after Liver Transplantation.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 28;11(4):e0154419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154419. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2019 Nov 26;14(11):e0225971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225971. PMID: 27123854 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Between Scylla and Charybdis: the role of the human immune system in the pathogenesis of hepatitis C.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Nov 28;19(44):7852-66. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.7852. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24307779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune regulation in chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016 Nov;51(11):1387-97. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2016.1170875. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27436030 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Expression of IL-1β and IL-18 Proinflammatory Interleukins Increases the Risk of Developing Cervical Cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019 Sep 1;20(9):2715-2721. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.9.2715. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019. PMID: 31554368 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive pathway map of IL-18-mediated signalling.J Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Jun;14(2):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s12079-019-00544-4. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 31863285 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome Expression in Gingival Crevicular Fluid of Patients with Periodontitis and Chronic Hepatitis C.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Nov 19;2021:6917919. doi: 10.1155/2021/6917919. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34840527 Free PMC article.
-
Residual HCV-RNA and Elevated Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predict Poor Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C After Treatment.Infect Dis Ther. 2025 Jan;14(1):305-315. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-01101-2. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Infect Dis Ther. 2025. PMID: 39725828 Free PMC article.
-
Association between interleukin-18 gene promoter (- 607C/A and - 137G/C) polymorphisms and chronic hepatitis C virus infections: A meta-analysis.Meta Gene. 2015 May 22;5:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2015.04.004. eCollection 2015 Sep. Meta Gene. 2015. PMID: 26042207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lauer GM, Walker BD. Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Seeff LB. Natural history of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;36(Suppl. 1):S35–46. - PubMed
-
- Shiffman ML. Optimizing the current therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus: peginterferon and ribavirin dosing and the utility of growth factors. Clin Liver Dis. 2008;12:487–505. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. IL-18: a Th1-inducing, proinflammatory cytokine and new member of the IL-1 family. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:11–24. - PubMed
-
- Okamura H, Tsutsui H, Komatsu T, et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-γ production by T cells. Nature. 1995;378:88–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

