Interleukin-12 is sufficient to promote antigen-independent interferon-gamma production by CD8 T cells in old mice
- PMID: 19740329
- PMCID: PMC2753923
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03061.x
Interleukin-12 is sufficient to promote antigen-independent interferon-gamma production by CD8 T cells in old mice
Abstract
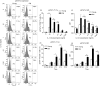
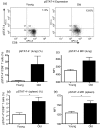
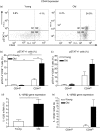
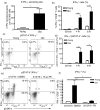
Numerous functional defects have been identified in naive T cells from aged mice, including deficiencies in proliferation, cytokine production and signal transduction. It is well documented that the ratio of naïve to memory T cells significantly decreases with age resulting in the majority of T cells from aged hosts expressing activated/memory T-cell markers (CD44(hi)), yet it is unclear whether T cells with a CD44(hi) phenotype in aged hosts are functionally equivalent to T cells with a similar phenotype in young hosts. We have identified a population of CD44(hi) CD8 T cells in old mice that are capable of secreting interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in response to interleukin-12 (IL-12) stimulation. This occurred in the absence of T-cell receptor engagement, a function that was not observed in CD8 T cells from young mice. This phenotype was associated with increased IL-12 receptor beta2 gene expression and IL-12 induced signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT-4) activation, even when CD8 T-cell numbers from young and old mice were normalized for CD44(hi) expression. Furthermore, we demonstrate that IL-12-induced STAT-4 activation was required for T helper type 1 (Th1) cytokine-induced IFN-gamma production in CD8 T cells. These data illustrate that old mice possess a specialized subset of CD44(hi) CD8 T cells with an enhanced responsiveness to IL-12, enabling these cells to produce substantial amounts of IFN-gamma in response to Th1 cytokine stimulation. We have therefore identified a functional difference in the populations of CD44(hi) CD8 T cells from young and old mice, and believe that understanding age-associated immunological changes is essential for helping the elderly combat deadly diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Beers NH, Berkow R. The Merck Manual of Geriatrics. 3rd edn. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck Research Laboratories; 2000.
-
- Niederman MS, Fein AM. Pneumonia in the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med. 1986;2:241–68. - PubMed
-
- Orme IM. Aging and immunity to tuberculosis: increased susceptibility of old mice reflects a decreased capacity to generate mediator T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987;138:4414–8. - PubMed
-
- Stead WW, Dutt AK. Tuberculosis in elderly persons. Annu Rev Med. 1991;42:267–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

