Dynamics of the CD8 T-cell response following yellow fever virus 17D immunization
- PMID: 19740333
- PMCID: PMC2753898
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03070.x
Dynamics of the CD8 T-cell response following yellow fever virus 17D immunization
Abstract
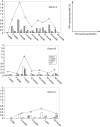
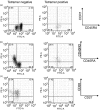
Management of yellow fever is focused on the prevention of illness by the use of the yellow fever virus (YFV) 17D vaccine. The role of neutralizing antibodies in protection is generally accepted with YFV-specific T cells likely contributing to the control of viral replication. We studied CD8(+) T-cell responses to four defined human leucocyte antigen-B35-restricted epitopes in YFV vaccine recipients as a model of the kinetics of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses to an acute human viral infection. Multiple features of these epitope-specific responses were analysed after vaccination including magnitude, cytokine production, phenotype and T-cell receptor repertoire. Peak peptide-specific interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) responses of almost 1% of CD8(+) T cells were seen as early as 2 weeks post-vaccination; however, dominant responses varied between donors. Peptide-specific responses were still detectable at 54 months post-vaccination. Tetramer-positive cells, at high frequencies, were detected as early as 7-9 days, before detectable IFN-gamma-producing cells, suggesting a defect in the functional capacity of some antigen-specific cells early post-vaccination. The predominant memory phenotype of the tetramer-positive population was a differentiated effector (CD45RA(+) CCR7(-) CD62L(-)) phenotype. The T-cell receptor Vbeta analysis revealed a diverse oligoclonal repertoire in tetramer-positive T-cell populations in two individuals. These characteristics of the YFV-specific T-cell response could contribute to vaccine effectiveness.
Figures


References
-
- Cheynier R, Langlade-Demoyen P, Marescot M, et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in the peripheral blood of children born to human immunodeficiency virus 1 infected mothers. Eur J Immunol. 1992;22:2211–7. - PubMed
-
- Riddell SR, Watanabe KS, Goodrich JM, Li CR, Agha MA, Greenberg PD. Restoration of viral immunity in immunodeficient humans by the adoptive transfer of T cell clones. Science. 1992;257:238–41. - PubMed
-
- Rooney CM, Smith CA, Ng CY, Loftin S, Li C, Krance RA, Brenner MK, Heselop HE. Use of gene modified virus specific T lymphocytes to control Epstein–Barr-virus related lynphoproliferation. Lancet. 1995;345:9–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

