Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 are phosphorylated at novel sites during varicella-zoster virus infection
- PMID: 19740981
- PMCID: PMC2772673
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01318-09
Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 are phosphorylated at novel sites during varicella-zoster virus infection
Abstract
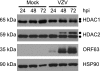
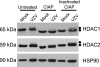
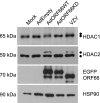
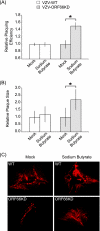
ORF66p, a virion-associated varicella-zoster virus (VZV) protein, is a member of a conserved Alphaherpesvirinae kinase family with homology to herpes simplex virus US3 kinase. Expression of ORF66p in cells infected with VZV or an adenovirus expressing only ORF66p results in hyperphosphorylation of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and HDAC2. Mapping studies reveal that phosphorylation is at a unique conserved Ser residue in the C terminus of both HDACs. This modification requires an active kinase domain in ORF66p, as neither protein is phosphorylated in cells infected with VZV lacking kinase activity. However, hyperphosphorylation appears to occur indirectly, as within the context of in vitro kinase reactions, purified ORF66p phosphorylates a peptide derived from ORF62p, a known substrate, but does not phosphorylate HDAC. These results support a model where ORF66p is necessary but not sufficient to effect hyperphosphorylation of HDAC1 and HDAC2.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 66 protein kinase and its relationship to alphaherpesvirus US3 kinases.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;342:79-98. doi: 10.1007/82_2009_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20186610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperphosphorylation of histone deacetylase 2 by alphaherpesvirus US3 kinases.J Virol. 2010 Oct;84(19):9666-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00981-10. Epub 2010 Jul 21. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20660201 Free PMC article.
-
The alphaherpesvirus US3/ORF66 protein kinases direct phosphorylation of the nuclear matrix protein matrin 3.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(1):568-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01611-10. Epub 2010 Oct 20. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 20962082 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of H2AX and ATM in varicella-zoster virus (VZV)-infected cells is associated with expression of specific VZV genes.Virology. 2014 Mar;452-453:52-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.12.039. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24606682 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC1 and HDAC2 in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos: Specificity versus compensation.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Jul;23(7):1119-27. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.31. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 27082454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic analyses of host-virus interactions during in vitro infection with wild-type and glycoprotein g-deficient (ΔgG) strains of ILTV in primary and continuous cell cultures.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 11;19(10):e0311874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311874. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39392810 Free PMC article.
-
Primary macrophages rely on histone deacetylase 1 and 2 expression to induce type I interferon in response to gammaherpesvirus infection.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(4):2268-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03278-13. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24335310 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 66 protein kinase and its relationship to alphaherpesvirus US3 kinases.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;342:79-98. doi: 10.1007/82_2009_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20186610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus UL29/28 protein interacts with components of the NuRD complex which promote accumulation of immediate-early RNA.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jun 24;6(6):e1000965. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000965. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20585571 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved gammaherpesvirus protein kinase targets histone deacetylases 1 and 2 to facilitate viral replication in primary macrophages.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(13):7314-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02713-12. Epub 2013 Apr 24. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23616648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

