The sympathetic nervous system modulates CD4(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells via a TGF-beta-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 19741161
- PMCID: PMC2780915
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0209107
The sympathetic nervous system modulates CD4(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells via a TGF-beta-dependent mechanism
Abstract
CD4(+)FoxP3(+) Tregs are essential mediators of the peripheral immune response to self-antigens. Accordingly, the homeostatic regulation of Treg activity and number would impact on the immune response to both self- and non-self antigens. Because the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) interacts chemically and physically with the central and peripheral immune system and exerts a direct influence on antigen-presenting cells and effector lymphocytes, we have investigated the effect of chemical ablation of the SNS on the number and function of peripheral Treg. Removal of murine peripheral sympathetic innervation by 6-hydroxydopamine induced an increase in splenic and lymph node CD4(+)FoxP3(+) Tregs by a TGF-beta-dependent mechanism. Further, this increase in Tregs coincides with an inhibition of the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Our results demonstrate that the SNS is an important contributor to the maintenance of peripheral Treg and TGF-beta acts as a bridge between the immune system and the nervous system. Neurological events mediated by the SNS, such as a stress response, may affect the number of T cells that regulate an immune response. Additionally, targeting Tregs via the SNS may be a novel approach to the prevention or treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Figures

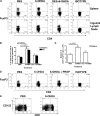
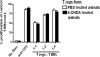
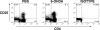

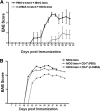
Comment in
-
Editorial: regulation of the regulator: sympathetic nervous system control of regulatory T cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2009 Dec;86(6):1269-70. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0409249. J Leukoc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19948519 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hogquist K A, Baldwin T A, Jameson S C. Central tolerance: learning self-control in the thymus. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:772–782. - PubMed
-
- Goodnow C C, Sprent J, Fazekas de St Groth B, Vinuesa C G. Cellular and genetic mechanisms of self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nature. 2005;435:590–597. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot J D, Gavin M A, Rudensky A Y. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–336. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:345–352. - PubMed
-
- Annacker O, Pimenta-Araujo R, Burlen-Defranoux O, Barbosa T C, Cumano A, Bandeira A. CD25+ CD4+ T cells regulate the expansion of peripheral CD4 T cells through the production of IL-10. J Immunol. 2001;166:3008–3018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

