Additive effects of genetic variation in GCK and G6PC2 on insulin secretion and fasting glucose
- PMID: 19741163
- PMCID: PMC2780888
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0228
Additive effects of genetic variation in GCK and G6PC2 on insulin secretion and fasting glucose
Abstract
Objective: Glucokinase (GCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 2 (G6PC2) regulate the glucose-cycling step in pancreatic beta-cells and may regulate insulin secretion. GCK rs1799884 and G6PC2 rs560887 have been independently associated with fasting glucose, but their interaction on glucose-insulin relationships is not well characterized.
Research design and methods: We tested whether these variants are associated with diabetes-related quantitative traits in Mexican Americans from the BetaGene Study and attempted to replicate our findings in Finnish men from the METabolic Syndrome in Men (METSIM) Study.
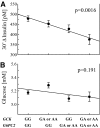
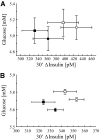
Results: rs1799884 was not associated with any quantitative trait (corrected P > 0.1), whereas rs560887 was significantly associated with the oral glucose tolerance test 30-min incremental insulin response (30' Deltainsulin, corrected P = 0.021). We found no association between quantitative traits and the multiplicative interaction between rs1799884 and rs560887 (P > 0.26). However, the additive effect of these single nucleotide polymorphisms was associated with fasting glucose (corrected P = 0.03) and 30' Deltainsulin (corrected P = 0.027). This additive association was replicated in METSIM (fasting glucose, P = 3.5 x 10(-10) 30' Deltainsulin, P = 0.028). When we examined the relationship between fasting glucose and 30' Deltainsulin stratified by GCK and G6PC2, we noted divergent changes in these quantitative traits for GCK but parallel changes for G6PC2. We observed a similar pattern in METSIM.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that variation in GCK and G6PC2 have additive effects on both fasting glucose and insulin secretion.
Figures
References
-
- Diabetes Genetics Initiative of Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Lund University and Novartis Institute for Biomedical Research Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science 2007; 316: 1331– 1336 - PubMed
-
- Zeggini E, Weedon MN, Lindgren CM, Frayling TM, Elliott KS, Lango H, Timpson NJ, Perry JRB, Rayner NW, Freathy RM, Barrett JC, Shields B, Morris AP, Ellard S, Groves CJ, Harries LW, Marchini JL, Owen KR, Knight B, Cardon LR, Walker M, Hitman GA, Morris AD, Doney ASF, The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. McCarthy MI, Hattersley AT: Replication of genome-wide association signals in U.K. samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 2007; 316: 1336– 1341 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, Dina C, Shen L, Serre D, Boutin P, Vincent D, Belisle A, Hadjadj S, Balkau B, Heude B, Charpentier G, Hudson TJ, Montpetit A, Pshezhetsky AV, Prentki M, Posner BI, Balding DJ, Meyre D, Polychronakos C, Froguel P: A genome-wide association study identified novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 2007; 445: 881– 885 - PubMed
-
- Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Jonsdottir T, Walters GB, Styrkarsdottir U, Gretarsdottir S, Emilsson V, Ghosh S, Baker A, Snorradottir S, Bjarnason H, Ng MCY, Hansen T, Bagger Y, Wilensky RL, Reilly MP, Adeyemo A, Chen Y, Zhou J, Gudnason V, Chen G, Huang H, Lashley K, Doumatey A, So W-Y, Ma RCY, Andersen G, Borch-Johnsen K, Jorgensen T, van Vliet-Ostaptchouk JV, Hofker MH, Wijmenga C, Christiansen C, Rader DJ, Rotimi C, Gurney M, Chan JCN, Pedersen O, Sigurdsson G, Gulcher JR, Thorsteinsdottir U, Kong A, Stefansson K: A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 770– 775 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

