HIV infection and the risk of cancers with and without a known infectious cause
- PMID: 19741479
- PMCID: PMC2863991
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283319184
HIV infection and the risk of cancers with and without a known infectious cause
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the risk of cancers with and without a known infectious cause in HIV-infected persons.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Methods: Adult HIV-infected and matched HIV-uninfected members of Kaiser Permanente followed between 1996 and 2007 for incident AIDS-defining cancers (ADCs), infection-related non-AIDS-defining cancers (NADCs; anal squamous cell, vagina/vulva, Hodgkin's lymphoma, penis, liver, human papillomavirus-related oral cavity/pharynx, stomach) and infection-unrelated NADC (all other NADCs).
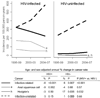
Results: We identified 20 277 HIV-infected and 202 313 HIV-uninfected persons. HIV-infected persons experienced 552 ADC, 221 infection-related NADC, and 388 infection-unrelated NADC. HIV-uninfected persons experienced 179 ADC, 284 infection-related NADC, and 3418 infection-unrelated NADC. The rate ratio comparing HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected persons for ADC was 37.7 [95% confidence interval (CI): 31.7-44.8], with decreases in the rate ratio over time (P < 0.001). The rate ratio for infection-related NADC was 9.2 (95% CI: 7.7-11.1), also with decreases in the rate ratio over time (P < 0.001). These results were largely influenced by anal squamous cell cancer and Hodgkin's lymphoma. The rate ratio for infection-unrelated NADC was 1.3 (95% CI: 1.2-1.4), with no change in the rate ratio over time (P = 0.44). Among infection-unrelated NADCs, other anal, skin, other head and neck, and lung cancer rates were higher and prostate cancer rates lower in HIV-infected persons. Among all infection-unrelated NADCs, the rate ratio decreased over time only for lung cancer (P = 0.007).
Conclusion: In comparison with those without HIV infection, HIV-infected persons are at particular risk for cancers with a known infectious cause, although the higher risk has decreased in the antiretroviral therapy era. Cancers without a known infectious cause are modestly increased in HIV-infected persons compared with HIV-uninfected persons.
Figures

References
-
- Engels EA, Biggar RJ, Hall HI, Cross H, Crutchfield A, Finch JL, et al. Cancer risk in people infected with human immunodeficiency virus in the United States. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg MJ, Neuhaus J, Bower M, Gey D, Hatzakis A, Henry K, et al. Risk of cancers during interrupted antiretroviral therapy in the SMART study. Aids. 2007;21:1957–1963. - PubMed
-
- Patel P, Hanson DL, Sullivan PS, Novak RM, Moorman AC, Tong TC, et al. Incidence of types of cancer among HIV-infected persons compared with the general population in the United States, 1992–2003. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:728–736. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg MJ, Abrams DI. AIDS-defining and non-AIDS-defining malignancies: cancer occurrence in the antiretroviral therapy era. Curr Opin Oncol. 2007;19:446–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

