Cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta(40) is decreased in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- PMID: 19743453
- PMCID: PMC3697750
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.21694
Cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta(40) is decreased in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Abstract
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy is caused by deposition of the amyloid beta protein in the cerebral vasculature. In analogy to previous observations in Alzheimer disease, we hypothesized that analysis of amyloid beta(40) and beta(42) proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid might serve as a molecular biomarker. We observed strongly decreased cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta(40) (p < 0.01 vs controls or Alzheimer disease) and amyloid beta(42) concentrations (p < 0.001 vs controls and p < 0.05 vs Alzheimer disease) in cerebral amyloid angiopathy patients. The combination of amyloid beta(42) and total tau discriminated cerebral amyloid angiopathy from controls, with an area under the receiver operator curve of 0.98. Our data are consistent with neuropathological evidence that amyloid beta(40) as well as amyloid beta(42) protein are selectively trapped in the cerebral vasculature from interstitial fluid drainage pathways that otherwise transport amyloid beta proteins toward the cerebrospinal fluid.
Figures
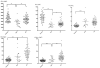
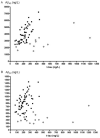
References
-
- Iwatsubo T, Odaka A, Suzuki N, Mizusawa H, Nukina N, Ihara Y. Visualization of Ab42(43) and Ab40 in senile plaques with end-specific monoclonals: evidence that an initially deposited species is Ab42(43) Neuron. 1994;13:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Savage MJ, Kawooya JK, Pinsker LR, et al. Elevated Ab levels in Alzheimer's disease brain are associated with selective accumulation of Ab42 in parenchymal amyloid plaques and both Ab40 and Ab42 in cerebrovascular deposits. Amyloid. 1995;2:234–240.
-
- Miller DL, Papayannopoulos IA, Styles J, et al. Peptide composition of the cerebrovascular and senile plaque core amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993;301:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Alonzo NC, Hyman BT, Rebeck GW, et al. Progression of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: accumulation of amyloid-beta40 in affected vessels. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998;57:353–359. - PubMed
-
- de Jong D, Kremer BP, Olde Rikkert MG, et al. Current state and future directions of neurochemical biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007;45:1421–1434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

