Conserved polar residues stabilize transmembrane domains and promote oligomerization in human nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3
- PMID: 19743837
- PMCID: PMC2758327
- DOI: 10.1021/bi900909g
Conserved polar residues stabilize transmembrane domains and promote oligomerization in human nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3
Abstract
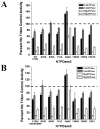
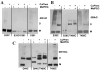
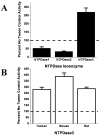
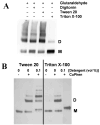
Polar residues play essential roles in the functions of transmembrane helices by mediating and stabilizing their helical interactions. To investigate the structural and functional roles of the conserved polar residues in the N- and C-terminal transmembrane helices of human nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3 (NTPDase3) (N-terminus, S33, S39, T41, and Q44; C-terminus, T490, T495, and C501), each was singly mutated to alanine. The mutant proteins were analyzed for enzymatic activities, glycosylation status, expression level, and Triton X-100 detergent sensitivity. The Q44A mutation decreased Mg-ATPase activity by approximately 70% and abolished Triton X-100 detergent inhibition of Ca-dependent nucleotidase activities while greatly attenuating Triton X-100 inhibition of Mg-dependent nucleotidase activities. The polar residues were also mutated to cysteine, singly and in pairs, to allow a disulfide cross-linking strategy to map potential inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bond interactions. The results support the centrality of Q44 for the strong intermolecular interactions driving the association of the N-terminal helices of two NTPDase3 monomers in a dimer, and the possibility that T41 may play a role in the specificity of this interaction. In addition, S33 and C501 form an intramolecular association, while S39 and T495 may contribute to helical interactions involved in forming higher-order oligomers. Lastly, Tween 20 substantially and selectively increases NTPDase3 activity, mediated by the transmembrane helices containing the conserved polar residues. Taken together, the data suggest a model for putative hydrogen bond interactions of the conserved polar residues in the transmembrane domain of native, oligomeric NTPDase3. These interactions are important for proper protein expression, full enzymatic activity, and susceptibility to membrane perturbations.
Figures




References
-
- Zimmermann H, Beaudoin AR, Bollen M, Goding JW, Guidotti G, Kirley TL, Robson SC, Sano K. In: Second International Workshop on Ecto-ATPases and Related Ectonucleotidases. Vanduffel L, editor. Shaker Publishing BV; Maastricht, The Netherlands, Diepenbeek, Belgium: 1999. pp. 1–9.
-
- Zimmermann H. Two novel families of ectonucleotidases: molecular structures, catalytic properties and a search for function. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999;20:231–236. - PubMed
-
- Wang T-F, Guidotti G. Golgi Localization and Functional Expression of Human Uridine Diphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:11392–11399. - PubMed
-
- Ivanenkov VV, Meller J, Kirley TL. Characterization of Disulfide Bonds in Human Nucleoside Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase 3 (NTPDase3): Implications for NTPDase Structural Modeling. Biochemistry. 2005;44:8998–9012. - PubMed
-
- Ivanenkov VV, Murphy-Piedmonte DM, Kirley TL. Bacterial Expression, Characterization, and Disulfide Bond Determination of Soluble Human NTPDase6 (CD39L2) Nucleotidase: Implications for Structure and Function. Biochemistry. 2003;42:11726–11735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

