S-Methadone augments R-methadone induced respiratory depression in the neonatal guinea pig
- PMID: 19744579
- PMCID: PMC2858643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2009.09.001
S-Methadone augments R-methadone induced respiratory depression in the neonatal guinea pig
Abstract
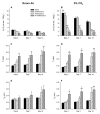
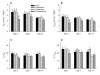
Methadone is administered as a racemic mixture, although its analgesic and respiratory effects are attributed to R-isomer activity at the mu opioid receptor (MOP). Recently, we observed a four-fold increase in inspiratory time in 3-day-old guinea pigs following an injection of racemic methadone. We hypothesized that this effect was due to augmentation of R-methadone induced respiratory depression by the S-methadone isomer. In the current longitudinal study, we injected 3-, 7-, and 14-day-old neonatal guinea pigs with saline, R-methadone, S-methadone, or R- plus S-methadone in order to characterize the roles of the individual isomers, as well as the synergistic effects of co-administration. Using plethysmography, we measured respiratory parameters while breathing room air and during a 5% CO(2) challenge. S-Methadone alone had no respiratory effects. However, the R- plus S-methadone group showed greater respiratory depression and increased inspiratory time than the R-methadone group in the youngest animals, suggesting that the respiratory effects of R-methadone are augmented by S-methadone in early development.
Figures


References
-
- Anand KJ. Pharmacological approaches to the management of pain in the neonatal intensive care unit. J. Perinatol. 2007;27(Suppl 1):S4–S11. - PubMed
-
- Blake MJ, Castro L, Leeder JS, Kearns GL. Ontogeny of drug metabolizing enzymes in the neonate. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2005;10:123–138. - PubMed
-
- Borday V, Foutz AS, Nordholm L, Denavit-Saubié M. Respiratory effects of glutamate receptor antagonists in neonate and adult mammals. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998;348:235–246. - PubMed
-
- Boulton DW, Arnaud P, Devane CL. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methadone enantiomers after a single oral dose of racemate. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001;70:48–57. - PubMed
-
- Cassus-Soulanis S, Foutz AS, Denavit-Saubié M. Involvement of NMDA receptors in inspiratory termination in rodents: effects of wakefulness. Brain Res. 1995;679:25–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

