Furanose-specific sugar transport: characterization of a bacterial galactofuranose-binding protein
- PMID: 19744923
- PMCID: PMC2781514
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.054296
Furanose-specific sugar transport: characterization of a bacterial galactofuranose-binding protein
Abstract
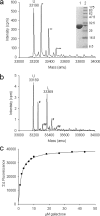
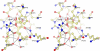
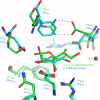
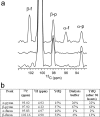
The widespread utilization of sugars by microbes is reflected in the diversity and multiplicity of cellular transporters used to acquire these compounds from the environment. The model bacterium Escherichia coli has numerous transporters that allow it to take up hexoses and pentoses, which recognize the more abundant pyranose forms of these sugars. Here we report the biochemical and structural characterization of a transporter protein YtfQ from E. coli that forms part of an uncharacterized ABC transporter system. Remarkably the crystal structure of this protein, solved to 1.2 A using x-ray crystallography, revealed that YtfQ binds a single molecule of galactofuranose in its ligand binding pocket. Selective binding of galactofuranose over galactopyranose was also observed using NMR methods that determined the form of the sugar released from the protein. The pattern of expression of the ytfQRTyjfF operon encoding this transporter mirrors that of the high affinity galactopyranose transporter of E. coli, suggesting that this bacterium has evolved complementary transporters that enable it to use all the available galactose present during carbon limiting conditions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural and functional characterization of a maltose/maltodextrin ABC transporter comprising a single solute binding domain (MalE) fused to the transmembrane subunit MalF.Res Microbiol. 2019 Jan-Feb;170(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2018.08.006. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Res Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30193862
-
Structure of D-allose binding protein from Escherichia coli bound to D-allose at 1.8 A resolution.J Mol Biol. 1999 Mar 12;286(5):1519-31. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2571. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10064713
-
Crystal structure of lactose permease in complex with an affinity inactivator yields unique insight into sugar recognition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 7;108(23):9361-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105687108. Epub 2011 May 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21593407 Free PMC article.
-
Structural comparison of lactose permease and the glycerol-3-phosphate antiporter: members of the major facilitator superfamily.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004 Aug;14(4):413-9. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.07.005. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15313234 Review.
-
Monosaccharide transporters in plants: structure, function and physiology.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 1;1465(1-2):263-74. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00143-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10748259 Review.
Cited by
-
Mining the Sinorhizobium meliloti transportome to develop FRET biosensors for sugars, dicarboxylates and cyclic polyols.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e43578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043578. Epub 2012 Sep 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028462 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Prediction of Resistance to Subinhibitory Antimicrobial Concentrations from Escherichia coli Genomes.mSystems. 2021 Aug 31;6(4):e0034621. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00346-21. Epub 2021 Aug 24. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34427505 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for a ribofuranosyl binding protein: insights into the furanose specific transport.Proteins. 2011 Apr;79(4):1352-7. doi: 10.1002/prot.22965. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Proteins. 2011. PMID: 21387413 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Characterization of the l-arabinofuranose-specific GafABCD ABC transporter essential for l-arabinose-dependent growth of the lignocellulose-degrading bacterium Shewanella sp. ANA-3.Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Mar;169(3):001308. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001308. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 36920280 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoelectronic Effects Impact Glycan Recognition.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Feb 5;142(5):2386-2395. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b11699. Epub 2020 Jan 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 31930911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ingraham J. L., Neidhardt F. C. (1987) Escherichia Coli and Salmonella Typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular Biology, American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C.
-
- Franchini A. G., Egli T. (2006) Microbiology 152, 2111–2127 - PubMed
-
- Liu M., Durfee T., Cabrera J. E., Zhao K., Jin D. J., Blattner F. R. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 15921–15927 - PubMed
-
- Siebold C., Flükiger K., Beutler R., Erni B. (2001) FEBS Lett. 504, 104–111 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

