Myopia affects retinal nerve fiber layer measurements as determined by optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 19745664
- PMCID: PMC2742764
- DOI: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e318193c2be
Myopia affects retinal nerve fiber layer measurements as determined by optical coherence tomography
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether increasing myopia is associated with thinner peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) when measured by Stratus optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Design: Observational cross-sectional study.
Methods: Normal subjects with myopia underwent refractometry, axial length measurement (IOL Master), optic nerve examination, and OCT (12 fast RNFL scans/eye). The more myopic eye was chosen as the study eye. Correlation coefficients were calculated for demographic and optic disk characteristics, and degree of myopia.
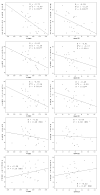
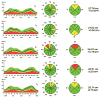
Results: Mean age (n=27) was 34+/-8 years (range: 23 to 54). Mean cup-to-disk ratio was 0.38 with 41% large and 59% medium disk size. Eight subjects had peripapillary atrophy and 6 had disk tilt. Mean spherical equivalent was -5.40 D (range: -1.25 to -11.25), with mean axial length of 25.65 mm (range: 22.63 to 27.92). No significant associations were found between RNFL thickness and age (P=0.20), sex, disk size, cup-to-disk ratio, tilt, or peripapillary atrophy. RNFL thickness decreased with higher axial length (overall R=-0.70, P<0.001, superior R=-0.60, P=0.001, and inferior R=-0.60, P=0.001), and higher spherical equivalent (overall R=-0.52, P=0.005, superior R=-0.41, P=0.03, and inferior R=-0.45, P=0.02). Overall RNFL thickness decreased 7 mum/1 mm of axial length, and 3 mum/1 D sphere.
Conclusions: Moderately myopic subjects tend to have thin peripapillary RNFL, mainly at the superior and inferior poles, as measured by Stratus OCT. This phenomenon should be considered when interpreting a glaucoma suspect's Stratus OCT measurements compared with the normative database.
Figures
References
-
- Wong TY, Klein BE, Klein R, et al. Refractive errors, intraocular pressure, and glaucoma in a white population. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P, Hourihan F, Sandbach J, Wang JJ. The relationship between glaucoma and myopia: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1999;106:2010–2015. - PubMed
-
- Xu L, Wang Y, Wang S, et al. High myopia and glaucoma susceptibility the Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:216–220. - PubMed
-
- Jonas JB, Dichtl A. Optic disc morphology in myopic primary open-angle glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1997;235:627–633. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Valenzuela E, Anderson NG, Pons M, Iezzi R. Retinal thickness by OCT in subjects with emmetropia, hyperopia, and myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43 E-Abstract 2574.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

