Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor inhibitor figitumumab (CP-751,871) in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin
- PMID: 19745765
- PMCID: PMC2941876
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ba2f1d
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor inhibitor figitumumab (CP-751,871) in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin
Abstract
Introduction: This phase 1 study was conducted to determine the recommended phase 2 dose of the selective insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor (IGF-IR) inhibitor figitumumab (F, CP-751,871) given in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors.
Methods: Patients received paclitaxel 200 mg/m2, carboplatin (area under the curve of 6), and F (0.05-20 mg/kg) q3 weeks for up to six cycles. Patients with objective response or stable disease were eligible to receive additional cycles of single agent F until disease progression. Safety, efficacy, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic endpoints were investigated.
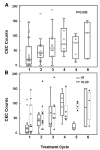
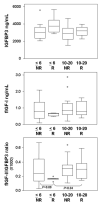
Results: Forty-two patients, including 35 with stages IIIB and IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), were enrolled in eight dose escalation cohorts. A maximum tolerated dose was not identified. Severe adverse events possibly related to F included fatigue, diarrhea, hyperglycemia, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase elevation, and thrombocytopenia (one case each). F plasma exposure parameters increased with dose. Fifteen objective responses (RECIST) were reported, including two complete responses in NSCLC and ovarian carcinoma. Notably, levels of bioactive IGF-1 seemed to influence response to treatment with objective responses in patients with a high baseline-free IGF-1 to IGF binding protein-3 ratio seen only in the 10 and 20 mg/kg dosing cohorts.
Conclusions: F was well tolerated in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin. Based on its favorable safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic properties, the maximal feasible dose of 20 mg/kg has been selected for further investigation.
Figures


References
-
- Pollak M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:915–928. - PubMed
-
- Favoni RE, De Cupis A, Ravera F, et al. Expression and function of the insulin like growth factor 1 system in human non small cell lung cancer and normal lung cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1994;56:858–866. - PubMed
-
- Spitz MR, Barnett MJ, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Wu X, Pollak M. Serum Insulin like growth factor (IGF) and IGF binding protein levels and risk of lung cancer: a case control study nested in the beta carotene and retinol efficacy trial cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002;11:1413–1418. - PubMed
-
- Cohen BD, Baker DA, Soderstrom C, et al. Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody figitumumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2063–2073. - PubMed
-
- de Bono JS, Scher HI, Montgomery RB, et al. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6302–6309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

