Correlation of pancreatic histopathologic findings and islet yield in children with chronic pancreatitis undergoing total pancreatectomy and islet autotransplantation
- PMID: 19745778
- PMCID: PMC7679082
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181b8ff71
Correlation of pancreatic histopathologic findings and islet yield in children with chronic pancreatitis undergoing total pancreatectomy and islet autotransplantation
Abstract
Objectives: The probability of insulin independence after intraportal islet autotransplantation (IAT) for chronic pancreatitis (CP) treated by total pancreatectomy (TP) relates to the number of islets isolated from the excised pancreas. Our goal was to correlate the islet yield with the histopathologic findings and the clinical parameters in pediatric (age, <19 years) CP patients undergoing TP-IAT.
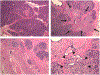
Methods: Eighteen pediatric CP patients aged 5 to 18 years (median, 15.6 years) who underwent TP-IAT were studied. Demographics and clinical history came from medical records. Histopathologic specimens from the pancreas were evaluated for presence and severity of fibrosis, acinar cell atrophy, inflammation, and nesidioblastosis by a surgical pathologist blinded to clinical information.
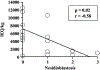
Results: Fibrosis and acinar atrophy negatively correlated with islet yield (P = 0.02, r = -0.50), particularly in hereditary CP (P = 0.01). Previous duct drainage surgeries also had a strong negative correlation (P = 0.01). Islet yield was better in younger (preteen) children (P = 0.02, r = -0.61) and in those with pancreatitis of shorter duration (P = 0.04, r = -0.39).
Conclusions: For preserving beta cell mass, it is best to perform TP-IAT early in the course of CP in children, and prior drainage procedures should be avoided to maximize the number of islets available, especially in hereditary disease.
Figures
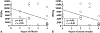
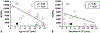
References
-
- Warshaw AL, Banks PA, Fernandez-Del CC. AGA technical review: treatment of pain in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1998;115(3):765–776. - PubMed
-
- Buscher HC, Jansen JB, van Dongen R, et al. Long-term results of bilateral thoracoscopic splanchnicectomy in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2002;89(2):158–162. - PubMed
-
- Dite P, Ruzicka M, Zboril V, et al. A prospective, randomized trial comparing endoscopic and surgical therapy for chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2003;35(7):553–558. - PubMed
-
- Cahen DL, Gouma DJ, Nio Y, et al. Endoscopic versus surgical drainage of the pancreatic duct in chronic pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356(7):676–684. - PubMed
-
- Frey CF, Suzuki M, Isaji S, et al. Pancreatic resection for chronic pancreatitis. Surg Clin North Am. 1989;69(3):499–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

