SnoN functions as a tumour suppressor by inducing premature senescence
- PMID: 19745809
- PMCID: PMC2782089
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.250
SnoN functions as a tumour suppressor by inducing premature senescence
Abstract
SnoN represses TGF-beta signalling to promote cell proliferation and has been defined as a proto-oncogene partly due to its elevated expression in many human cancer cells. Although the anti-tumourigenic activity of SnoN has been suggested, the molecular basis for this has not been defined. We showed here that high levels of SnoN exert anti-oncogenic activity by inducing senescence. SnoN interacts with the promyelocytic leukaemia (PML) protein and is recruited to the PML nuclear bodies where it stabilizes p53, leading to premature senescence. Furthermore, overexpression of SnoN inhibits oncogenic transformation induced by Ras and Myc in vitro and significantly blocks papilloma development in vivo in a carcinogen-induced skin tumourigenesis model. The few papillomas that were developed displayed high levels of senescence and spontaneously regressed. Our study has revealed a novel Smad-independent pathway of SnoN function that mediates its anti-oncogenic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
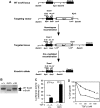
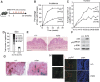
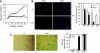





Comment in
-
Oncogene and tumour suppressor: the two faces of SnoN.EMBO J. 2009 Nov 18;28(22):3459-60. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.311. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19920850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC, Takaoka M, Nakagawa H, Tort F, Fugger K, Johansson F, Sehested M, Andersen CL, Dyrskjot L, Orntoft T, Lukas J et al. (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature 444: 633–637 - PubMed
-
- Bernardi R, Pandolfi PP (2007) Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 1006–1016 - PubMed
-
- Blasco MA, Lee HW, Hande MP, Samper E, Lansdorp PM, DePinho RA, Greider CW (1997) Telomere shortening and tumor formation by mouse cells lacking telomerase RNA. Cell 91: 25–34 - PubMed
-
- Bode AM, Dong Z (2004) Post-translational modification of p53 in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 793–805 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

