Effects of chronic mild stress on the development of atherosclerosis and expression of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in adolescent apolipoprotein E knockout mice
- PMID: 19746160
- PMCID: PMC2734999
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/613879
Effects of chronic mild stress on the development of atherosclerosis and expression of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in adolescent apolipoprotein E knockout mice
Abstract
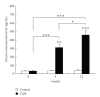
Here, we investigated the effect of chronic mild stress (CMS) on the development of atherosclerosis as well as the expression of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) signaling pathway in adolescent apolipoprotein E knockout (apoE-/-) mice. Mice were subjected to daily CMS for 0, 4, and 12 weeks, respectively. To identify the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in adolescent apolipoprotein E knockout mice subjected to CMS, we compared gene expression in aortas of stressed and unstressed mice using TLRs signaling pathway real-time PCR microarrays consisting of 87 genes. We found that atherosclerosis lesions both in aortic tress and sinuses of CMS mice were significantly increased linearly in response to duration of CMS exposure. Among 87 genes analyzed, 15 genes were upregulated in stressed mice, especially TLR4, myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), and IL-1beta, and 28 genes were downregulated compared with nonstressed mice. CMS mice demonstrated markedly increased aortic atherosclerosis that were associated with significant increases in levels of expression of TLR4, MyD88, nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), MCP-1, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and sICAM-1. Taken together, our results suggest an important role for TLR4 signaling pathway in atherosclerosis in a CMS mouse model.
Figures







References
-
- Rozanski A, Blumenthal JA, Kaplan J. Impact of psychological factors on the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and implications for therapy. Circulation. 1999;99(16):2192–2217. - PubMed
-
- Xu XH, Shah PK, Faure E, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 is expressed by macrophages in murine and human lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques and upregulated by oxLDL. Circulation. 2001;104(25):3103–3108. Article ID 10.1161/hc5001.100631. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan JR, Manuck SB, Clarkson TB, et al. Social stress and atherosclerosis in normocholesterolemic monkeys. Science. 1983;220(4598):733–735. - PubMed
-
- Rozanski A, Blumenthal JA, Davidson KW, et al. The epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management of psychosocial risk factors in cardiac practice: the emerging field of behavioral cardiology. Journal of American College of Cardiology. 2005;45(5):637–651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

