Clara cell: progenitor for the bronchiolar epithelium
- PMID: 19747565
- PMCID: PMC2787899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.09.002
Clara cell: progenitor for the bronchiolar epithelium
Abstract
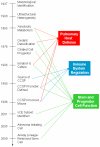
Clara cells were first described as a morphologically distinct cell type by Kolliker in 1881, but they take their name from the seminal study of human and rabbit bronchioles by Max Clara in 1937. Since their discovery, Clara cells have been identified as central players in protecting the airway from environmental exposures. The diverse functions of Clara cells in lung homeostasis include roles in xenobiotic metabolism, immune system regulation, and progenitor cell activity. Recent identification of a sub-population of Clara cells as a bronchiolar tissue-specific stem cell and a potential tumor initiating cell has focused the attention of cell and molecular biologists on the Clara cell and its behavior under normal and disease conditions.
Figures



References
-
- Hoyt RF, Jr., McNelly NA, McDowell EM, Sorokin SP. Neuroepithelial bodies stimulate proliferation of airway epithelium in fetal hamster lung. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:L234–240. - PubMed
-
- Ito T, Udaka N, Yazawa T, Okudela K, Hayashi H, Sudo T, Guillemot F, Kageyama R, Kitamura H. Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors regulate the neuroendocrine differentiation of fetal mouse pulmonary epithelium. Development. 2000;127:3913–3921. - PubMed
-
- Khoor A, Gray ME, Singh G, Stahlman MT. Ontogeny of Clara cell-specific protein and its mRNA: their association with neuroepithelial bodies in human fetal lung and in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Histochem Cytochem. 1996;44:1429–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

