An intersubunit signaling network coordinates ATP hydrolysis by m-AAA proteases
- PMID: 19748354
- PMCID: PMC2744646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.07.018
An intersubunit signaling network coordinates ATP hydrolysis by m-AAA proteases
Abstract
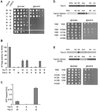
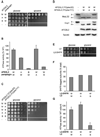
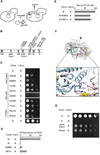
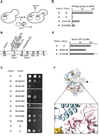
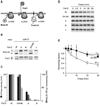
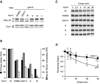
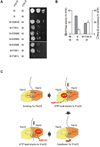
Ring-shaped AAA+ ATPases control a variety of cellular processes by substrate unfolding and remodeling of macromolecular structures. However, how ATP hydrolysis within AAA+ rings is regulated and coupled to mechanical work is poorly understood. Here we demonstrate coordinated ATP hydrolysis within m-AAA protease ring complexes, conserved AAA+ machines in the inner membrane of mitochondria. ATP binding to one AAA subunit inhibits ATP hydrolysis by the neighboring subunit, leading to coordinated rather than stochastic ATP hydrolysis within the AAA ring. Unbiased genetic screens define an intersubunit signaling pathway involving conserved AAA motifs and reveal an intimate coupling of ATPase activities to central AAA pore loops. Coordinated ATP hydrolysis between adjacent subunits is required for membrane dislocation of substrates, but not for substrate processing. These findings provide insight into how AAA+ proteins convert energy derived from ATP hydrolysis into mechanical work.
Figures
Comment in
-
The alternating power stroke of a 6-cylinder AAA protease chaperone engine.Mol Cell. 2009 Sep 11;35(5):545-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.08.013. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19748349
References
-
- Arlt H, Tauer R, Feldmann H, Neupert W, Langer T. The YTA10-12-complex, an AAA protease with chaperone-like activity in the inner membrane of mitochondria. Cell. 1996;85:875–885. - PubMed
-
- Bolon DN, Grant RA, Baker TA, Sauer RT. Nucleotide-dependent substrate handoff from the SspB adaptor to the AAA+ ClpXP protease. Mol. Cell. 2004;16:343–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

