miR-24 Inhibits cell proliferation by targeting E2F2, MYC, and other cell-cycle genes via binding to "seedless" 3'UTR microRNA recognition elements
- PMID: 19748357
- PMCID: PMC2757794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.08.020
miR-24 Inhibits cell proliferation by targeting E2F2, MYC, and other cell-cycle genes via binding to "seedless" 3'UTR microRNA recognition elements
Abstract
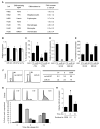
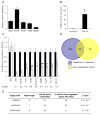
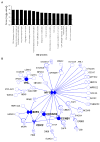
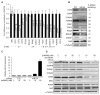
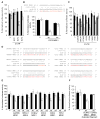
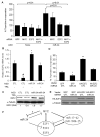
miR-24, upregulated during terminal differentiation of multiple lineages, inhibits cell-cycle progression. Antagonizing miR-24 restores postmitotic cell proliferation and enhances fibroblast proliferation, whereas overexpressing miR-24 increases the G1 compartment. The 248 mRNAs downregulated upon miR-24 overexpression are highly enriched for DNA repair and cell-cycle regulatory genes that form a direct interaction network with prominent nodes at genes that enhance (MYC, E2F2, CCNB1, and CDC2) or inhibit (p27Kip1 and VHL) cell-cycle progression. miR-24 directly regulates MYC and E2F2 and some genes that they transactivate. Enhanced proliferation from antagonizing miR-24 is abrogated by knocking down E2F2, but not MYC, and cell proliferation, inhibited by miR-24 overexpression, is rescued by miR-24-insensitive E2F2. Therefore, E2F2 is a critical miR-24 target. The E2F2 3'UTR lacks a predicted miR-24 recognition element. In fact, miR-24 regulates expression of E2F2, MYC, AURKB, CCNA2, CDC2, CDK4, and FEN1 by recognizing seedless but highly complementary sequences.
Figures
 ; enzyme,
; enzyme,  ; kinase,
; kinase,  ; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor,
; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor,  ; transporter,
; transporter,  ; phosphatase,
; phosphatase,  ; peptidase,
; peptidase,  ; translation regulator,
; translation regulator,  ; other, ●).
; other, ●).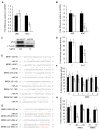
References
-
- Bracken AP, Ciro M, Cocito A, Helin K. E2F target genes: unraveling the biology. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:409–417. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, et al. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1793–1801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

