The interaction of NSBP1/HMGN5 with nucleosomes in euchromatin counteracts linker histone-mediated chromatin compaction and modulates transcription
- PMID: 19748358
- PMCID: PMC2757144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.07.002
The interaction of NSBP1/HMGN5 with nucleosomes in euchromatin counteracts linker histone-mediated chromatin compaction and modulates transcription
Abstract
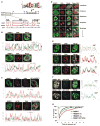
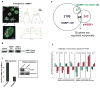
Structural changes in specific chromatin domains are essential to the orderly progression of numerous nuclear processes, including transcription. We report that the nuclear protein NSBP1 (HMGN5), a recently discovered member of the HMGN nucleosome-binding protein family, is specifically targeted by its C-terminal domain to nucleosomes in euchromatin. We find that the interaction of NSBP1 with nucleosomes alters the compaction of cellular chromatin and that in living cells, NSBP1 interacts with linker histones. We demonstrate that the negatively charged C-terminal domain of NSBP1 interacts with the positively charged C-terminal domain of H5 and that NSBP1 counteracts the linker histone-mediated compaction of a nucleosomal array. Dysregulation of the cellular levels of NSBP1 alters the transcription level of numerous genes. We suggest that mouse NSBP1 is an architectural protein that binds preferentially to euchromatin and modulates the fidelity of the cellular transcription profile by counteracting the chromatin-condensing activity of linker histones.
Figures





References
-
- Alfonso PJ, Crippa MP, Hayes JJ, Bustin M. The footprint of chromosomal proteins HMG-14 and HMG-17 on chromatin subunits. J Mol Biol. 1994;236:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi ME, Agresti A. HMG proteins: dynamic players in gene regulation and differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:496–506. - PubMed
-
- Bustin M. Chromatin unfolding and activation by HMGN(*) chromosomal proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:431–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

