Recruitment of fanconi anemia and breast cancer proteins to DNA damage sites is differentially governed by replication
- PMID: 19748364
- PMCID: PMC2758766
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.034
Recruitment of fanconi anemia and breast cancer proteins to DNA damage sites is differentially governed by replication
Abstract
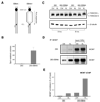
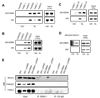
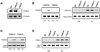
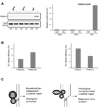
Fanconi anemia (FA) is characterized by cellular hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinking agents, but how the Fanconi pathway protects cells from DNA crosslinks and whether FA proteins act directly on crosslinks remain unclear. We developed a chromatin-IP-based strategy termed eChIP and detected association of multiple FA proteins with DNA crosslinks in vivo. Interdependence analyses revealed that crosslink-specific enrichment of various FA proteins is controlled by distinct mechanisms. BRCA-related FA proteins (BRCA2, FANCJ/BACH1, and FANCN/PALB2), but not FA core and I/D2 complexes, require replication for their crosslink association. FANCD2, but not FANCJ and FANCN, requires the FA core complex for its recruitment. FA core complex requires nucleotide excision repair proteins XPA and XPC for its association. Consistent with the distinct recruitment mechanism, recombination-independent crosslink repair was inversely affected in cells deficient of FANC-core versus BRCA-related FA proteins. Thus, FA proteins participate in distinct DNA damage response mechanisms governed by DNA replication status.
Figures
References
-
- Alpi AF, Pace PE, Babu MM, Patel KJ. Mechanistic insight into site-restricted monoubiquitination of FANCD2 by Ube2t, FANCL, and FANCI. Mol Cell. 2008;32:767–777. - PubMed
-
- Ciccia A, Ling C, Coulthard R, Yan Z, Xue Y, Meetei AR, Laghmani el H, Joenje H, McDonald N, de Winter JP, et al. Identification of FAAP24, a Fanconi anemia core complex protein that interacts with FANCM. Mol Cell. 2007;25:331–343. - PubMed
-
- Erkko H, Xia B, Nikkila J, Schleutker J, Syrjakoski K, Mannermaa A, Kallioniemi A, Pylkas K, Karppinen SM, Rapakko K, et al. A recurrent mutation in PALB2 in Finnish cancer families. Nature. 2007;446:316–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

