Estrogen exposure, obesity and thyroid disease in women with severe pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 19748850
- PMCID: PMC3352226
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-10-433
Estrogen exposure, obesity and thyroid disease in women with severe pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
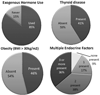
Severe pulmonary hypertension is a lethal group of disorders which preferentially afflicts women. It appears that in recent years the patient profile has shifted towards older, obese, and postmenopausal women, suggesting that endocrine factors may be important. Several studies have revealed an increased prevalence of thyroid disease in these patients, but no studies have evaluated for a coexistence of endocrine factors. In particular, no studies have attempted to evaluate for concurrent thyroid disease, obesity and long-term estrogen exposure in patients. 88 patients attending the Pulmonary Hypertension Association 8th International meeting completed a questionnaire and were interviewed. Information was collected regarding reproductive history, height, weight, and previous diagnosis of thyroid disease. 46% met criteria for obesity. 41% reported a diagnosis of thyroid disease. 81% of women reported prior use of hormone therapy. 70% reported greater than 10 years of exogenous hormone use. 74% of female patients reported two or more of potentially disease modifying endocrine factors (obesity, thyroid disease or estrogen therapy). The coexistent high prevalence in our cohort of exogenous estrogen exposure, thyroid disease and obesity suggests that an interaction of multiple endocrine factors might contribute to the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension and may represent epigenetic modifiers in genetically-susceptible individuals.
Figures
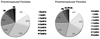

References
-
- Simonneau G, Galie N, Rubin LJ, Langleben D, Seeger W, Domenighetti G. et al.Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(12 Suppl S):5S–12S. - PubMed
-
- Voelkel NF, Reeves JT. Primary Pulmonary Hypertension in Pulmonary Vascular Diseases. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1979. Lung Biology in Health and Disease; pp. 573–628.
-
- Rich S, Dantzker DR, Ayres SM, Bergofsky EH, Brundage BH, Detre KM. et al.Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1987;107(2):216–23. - PubMed
-
- Badesch DB, Benza RL, Krichman AM, Raskob GE, Giles S. Reveal registry: baseline characteristics of the first 1,226 enrolled patients. Chest Meeting Abstracts. 2007;132(4):473b–474.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

