YjhS (NanS) is required for Escherichia coli to grow on 9-O-acetylated N-acetylneuraminic acid
- PMID: 19749043
- PMCID: PMC2772488
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01000-09
YjhS (NanS) is required for Escherichia coli to grow on 9-O-acetylated N-acetylneuraminic acid
Abstract
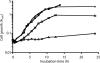
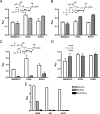
The nanATEK-yhcH, yjhATS, and yjhBC operons in Escherichia coli are coregulated by environmental N-acetylneuraminic acid, the most prevalent sialic acid in nature. Here we show that YjhS (NanS) is a probable 9-O-acetyl N-acetylneuraminic acid esterase required for E. coli to grow on this alternative sialic acid, which is commonly found in mammalian host mucosal sites.
Figures
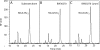

Similar articles
-
Unexpected Diversity of Escherichia coli Sialate O-Acetyl Esterase NanS.J Bacteriol. 2016 Sep 22;198(20):2803-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00189-16. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27481927 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the Escherichia coli sialoregulon by transcriptional repressor NanR.J Bacteriol. 2013 Oct;195(20):4689-701. doi: 10.1128/JB.00692-13. Epub 2013 Aug 9. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23935044 Free PMC article.
-
De-O-Acetylation of mucin-derived sialic acids by recombinant NanS-p esterases of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL933.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Dec;308(8):1113-1120. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30340996 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of microbial sialic acid metabolism.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004 Mar;68(1):132-53. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.1.132-153.2004. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15007099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sialic acid diversity in the human gut: Molecular impacts and tools for future discovery.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022 Aug;75:102397. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102397. Epub 2022 May 30. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 35653953 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of sialidase in glycoprotein utilization by Tannerella forsythia.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Nov;157(Pt 11):3195-3202. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.052498-0. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21885482 Free PMC article.
-
Growth media simulating ileal and colonic environments affect the intracellular proteome and carbon fluxes of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL933.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Jun;79(12):3703-15. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-13. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23563955 Free PMC article.
-
Social-Stress-Responsive Microbiota Induces Stimulation of Self-Reactive Effector T Helper Cells.mSystems. 2019 May 14;4(4):e00292-18. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00292-18. eCollection 2019 Jul-Aug. mSystems. 2019. PMID: 31098398 Free PMC article.
-
"Just a spoonful of sugar...": import of sialic acid across bacterial cell membranes.Biophys Rev. 2018 Apr;10(2):219-227. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0343-x. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 29222808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sialic acid, periodontal pathogens and Tannerella forsythia: stick around and enjoy the feast!Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012 Feb;27(1):11-22. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2011.00630.x. Epub 2011 Nov 12. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22230462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baba, T., T. Ara, M. Hasegawa, Y. Takai, Y. Okumura, M. Baba, K. A. Datsenko, M. Tomita, B. L. Wanner, and H. Mori. 21 February 2006, posting date. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. doi:10.1038/msb4100050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker, D., M. Selbach, C. Rollenhagen, M. Ballmaier, T. F. Meyer, M. Mann, and D. Bumann. 2006. Robust Salmonella metabolism limits possibilities for new antimicrobials. Nature 440:303-307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

