Myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury is dependent on both IgM and mannose-binding lectin
- PMID: 19749170
- PMCID: PMC2781373
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00049.2009
Myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury is dependent on both IgM and mannose-binding lectin
Abstract
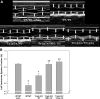
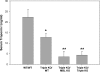
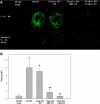
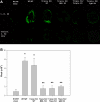
Complement activation has been shown to play an important role in the inflammation and tissue injury following myocardial ischemia and reperfusion (MI/R). Several recent studies from our laboratory demonstrated the importance of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) as the initiation pathway for complement activation and the resulting pathological effects following MI/R. However, other studies from the past suggest an important role of the classical pathway and perhaps natural antibodies. In the present study, we used newly generated genetically modified mice that lack secreted IgM (sIgM), MBL-A, and MBL-C (sIgM/MBL null) in a plasma reconstitution mouse model of MI/R. Following 30 min of ischemia and 4 h of reperfusion, left ventricular ejection fractions were significantly higher in sIgM/MBL null mice reconstituted with MBL null or sIgM/MBL null plasma compared with reconstitution with wild-type (WT) plasma or WT mice reconstituted with WT plasma following MI/R. Serum troponin I concentration, myocardial polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration, and C3 deposition were dependent on the combined presence of sIgM and MBL. These results demonstrate that MI/R-induced complement activation, inflammation, and subsequent tissue injury require both IgM and MBL. Thus MBL-dependent activation of the lectin pathway may not be completely antibody independent in I/R models.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mannose-binding lectin binds IgM to activate the lectin complement pathway in vitro and in vivo.Immunobiology. 2006;211(10):759-66. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2006.06.011. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Immunobiology. 2006. PMID: 17113913
-
Mannose-binding lectin is a regulator of inflammation that accompanies myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury.J Immunol. 2005 Jul 1;175(1):541-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.541. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15972690
-
Mannose-binding lectin plays a critical role in myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion injury in a mouse model of diabetes.Diabetologia. 2008 Aug;51(8):1544-51. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1044-6. Epub 2008 May 21. Diabetologia. 2008. PMID: 18493734 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) and vascular complications in diabetes.Horm Metab Res. 2005 Apr;37 Suppl 1:95-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-861372. Horm Metab Res. 2005. PMID: 15918118 Review.
-
Emerging role of the mannose-binding lectin-dependent pathway of complement activation in clinical organ transplantation.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011 Feb;16(1):28-33. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e3283425509. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21157341 Review.
Cited by
-
Complement activation and cardiac surgery: a novel target for improving outcomes.Anesth Analg. 2012 Oct;115(4):759-71. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182652b7d. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Anesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22798530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment with Cobra Venom Factor Decreases Ischemic Tissue Damage in Mice.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 29;12(2):309. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020309. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397911 Free PMC article.
-
Complement and Transplantation: From New Mechanisms to Potential Biomarkers and Novel Treatment Strategies.Clin Lab Med. 2019 Mar;39(1):31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2018.10.004. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Clin Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 30709507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Healing the Broken Heart; The Immunomodulatory Effects of Stem Cell Therapy.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 9;11:639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00639. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32328072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Secretory Activity Molecules of Visceral Adipocytes in Abdominal Obesity in the Development of Cardiovascular Disease: A Review.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 28;10(3):374. doi: 10.3390/biom10030374. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32121175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong PW, Mahaffey KW, Chang WC, Weaver WD, Hochman JS, Theroux P, Rollins S, Todaro TG, Granger CB, COMMA Investigators Concerning the mechanism of pexelizumab's benefit in acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 151: 787–790, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Austen WG, Jr, Kobzik L, Carroll MC, Hechtman HB, Moore FD., Jr The role of complement and natural antibody in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 16: 1–8, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Buerke M, Murohara T, Lefer AM. Cardioprotective effects of a C1 esterase inhibitor in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation 91: 393–402, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Buerke M, Prüfer D, Dahm M, Oelert H, Meyer J, Darius H. Blocking of classical complement pathway inhibits endothelial adhesion molecule expression and preserves ischemic myocardium from reperfusion injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286: 429–438, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Buerke M, Schwertz H, Seitz W, Meyer J, Darius H. Novel small molecule inhibitor of C1s exerts cardioprotective effects in ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbits. J Immunol 167: 5375–5380, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

