Neuroimaging and deep brain stimulation
- PMID: 19749225
- PMCID: PMC7964047
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1644
Neuroimaging and deep brain stimulation
Abstract
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a new neurosurgical method principally used for the treatment of Parkinson disease (PD). Many new applications of DBS are under development, including the treatment of intractable psychiatric diseases. Brain imaging is used for the selection of patients for DBS, to localize the target nucleus, to detect complications, and to evaluate the final electrode contact position. In patients with implanted DBS systems, there is a risk of electrode heating when MR imaging is performed. This contraindicates MR imaging unless specific precautions are taken. Involvement of neuroradiologists in DBS procedures is essential to optimize presurgical evaluation, targeting, and postoperative anatomic results. The precision of the neuroradiologic correlation with anatomic data and clinical outcomes in DBS promises to yield significant basic science and clinical advances in the future.
Figures

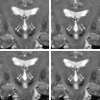

References
-
- Benabid AL, Pollak P, Gervason C, et al. . Long-term suppression of tremor by chronic stimulation of the ventral intermediate thalamic nucleus. Lancet 1991; 337: 403–06 - PubMed
-
- Limousin P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, et al. . Effect of parkinsonian signs and symptoms of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Lancet 1995; 345: 91–95 - PubMed
-
- Landi A, Parolin M, Piolti R, et al. . Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson's disease: the experience of the Neurosurgical Department in Monza. Neurol Sci 2003; 24: (suppl 1) S43–44 - PubMed
-
- Loher TJ, Burgunder JM, Pohle T, et al. . Long-term pallidal deep brain stimulation in patients with advanced Parkinson disease: 1-year follow-up study. J Neurosurg 2002; 96: 844–53 - PubMed
-
- Welter ML, Houeto JL, Tezenas du Montcel S, et al. . Clinical predictive factors of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Brain 2002; 125: 575–83 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
