Molecular signatures of disease brain endothelia provide new sites for CNS-directed enzyme therapy
- PMID: 19749771
- PMCID: PMC3181494
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2025
Molecular signatures of disease brain endothelia provide new sites for CNS-directed enzyme therapy
Abstract
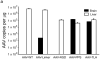
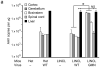
The brain vasculature forms an immense network such that most neural cells are in contact with a microvessel. Here we tested the hypothesis that endothelia lining these vessels can be harnessed to create a cellular reservoir of enzyme replacement therapy to diseased brain. As a model system, we used mice with central nervous system (CNS) deficits due to lysosomal storage disease (LSD mice). The basic premise of this work is that recombinant enzyme expressed in, and secreted from, the vascular endothelia will be endocytosed by underlying neurons and glia, decreasing neuropathology. We screened a phage library in vivo by panning to identify peptides that bound the vascular endothelia in diseased and wild-type mice. Epitopes binding diseased brain were distinct from those panned from normal brain. Moreover, different epitopes were identified in two distinct LSD disease models, implying a unique vascular signature imparted by the disease state. Presentation of these epitopes on the capsid of adeno-associated virus (AAV) expanded the biodistribution of intravenously injected AAV from predominantly liver to include the CNS. Peripheral injection of the epitope-modified AAVs expressing the enzymes lacking in LSD mice reconstituted enzyme activity throughout the brain and improved disease phenotypes in two distinct disease models.
Figures











Comment in
-
Gateway to the diseased brain.Nat Med. 2009 Oct;15(10):1123-4. doi: 10.1038/nm1009-1123. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19812565 No abstract available.
References
-
- Work LM, et al. Vascular bed-targeted in vivo gene delivery using tropism-modified adeno-associated viruses. Mol Ther. 2006;13:683–693. - PubMed
-
- Grifman M, et al. Incorporation of tumor-targeting peptides into recombinant adeno-associated virus capsids. Molecular Therapy. 2001;3(6):964–975. - PubMed
-
- Muller OJ, et al. Random peptide libraries displayed on adeno-associated virus to select for targeted gene therapy vectors. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:1040–1046. - PubMed
-
- Vogler C, et al. A novel model of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII due to an intracisternal a particle element transposition into the beta-glucuronidase gene: clinical and pathologic findings. Pediatr Res. 2001;49:342–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

