Genetic loss of D-amino acid oxidase activity reverses schizophrenia-like phenotypes in mice
- PMID: 19751394
- PMCID: PMC2824030
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2009.00529.x
Genetic loss of D-amino acid oxidase activity reverses schizophrenia-like phenotypes in mice
Abstract
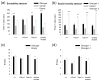
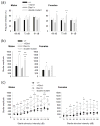
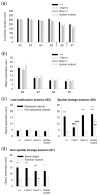
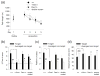
Reduced function of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) has been implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. The NMDAR contains a glycine binding site in its NR1 subunit that may be a useful target for the treatment of schizophrenia. In this study, we assessed the therapeutic potential of long-term increases in the brain levels of the endogenous NMDAR glycine site agonist D-serine, through the genetic inactivation of its catabolic enzyme D-amino acid oxidase (DAO) in mice. The effects of eliminating DAO function were investigated in mice that display schizophrenia-related behavioral deficits due to a mutation (Grin 1(D481N)) in the NR1 subunit that results in a reduction in NMDAR glycine affinity. Grin 1(D481N) mice show deficits in sociability, prolonged latent inhibition, enhanced startle reactivity and impaired spatial memory. The hypofunctional Dao 1(G181R) mutation elevated brain levels of D-serine, but alone it did not affect performance in the behavioral measures. Compared to animals with only the Grin 1(D481N) mutation, mice with both the Dao1(G181R) and Grin 1(D481N) mutations displayed an improvement in social approach and spatial memory retention, as well as a reversal of abnormally persistent latent inhibition and a partial normalization of startle responses. Thus, an increased level of D-serine resulting from decreased catalysis corrected the performance of mice with deficient NMDAR glycine site activation in behavioral tasks relevant to the negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Diminished DAO activity and elevations in D-serine may serve as an effective therapeutic intervention for the treatment of psychiatric symptoms.
Figures

References
-
- Adage T, Trillat AC, Quattropani A, et al. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological profile of AS057278, a selective d-amino acid oxidase inhibitor with potential anti-psychotic properties. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;18:200–214. - PubMed
-
- Almond SL, Fradley RL, Armstrong EJ, et al. Behavioral and biochemical characterization of a mutant mouse strain lacking D-amino acid oxidase activity and its implications for schizophrenia. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006;32:324–334. - PubMed
-
- Bendikov I, Nadri C, Amar S, et al. A CSF and postmortem brain study of D-serine metabolic parameters in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2007;90:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Berman I, Viegner B, Merson A, Allan E, Pappas D, Green AI. Differential relationships between positive and negative symptoms and neuropsychological deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 1997;25:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

