Regulation of dynein-driven microtubule sliding by the axonemal protein kinase CK1 in Chlamydomonas flagella
- PMID: 19752022
- PMCID: PMC2753152
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200906168
Regulation of dynein-driven microtubule sliding by the axonemal protein kinase CK1 in Chlamydomonas flagella
Abstract
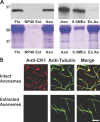
Experimental analysis of isolated ciliary/flagellar axonemes has implicated the protein kinase casein kinase I (CK1) in regulation of dynein. To test this hypothesis, we developed a novel in vitro reconstitution approach using purified recombinant Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CK1, together with CK1-depleted axonemes from the paralyzed flagellar mutant pf17, which is defective in radial spokes and impaired in dynein-driven microtubule sliding. The CK1 inhibitors (DRB and CK1-7) and solubilization of CK1 restored microtubule sliding in pf17 axonemes, which is consistent with an inhibitory role for CK1. The phosphatase inhibitor microcystin-LR blocked rescue of microtubule sliding, indicating that the axonemal phosphatases, required for rescue, were retained in the CK1-depleted axonemes. Reconstitution of depleted axonemes with purified, recombinant CK1 restored inhibition of microtubule sliding in a DRB- and CK1-7-sensitive manner. In contrast, a purified "kinase-dead" CK1 failed to restore inhibition. These results firmly establish that an axonemal CK1 regulates dynein activity and flagellar motility.
Figures
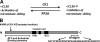
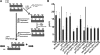
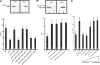
Similar articles
-
Regulation of flagellar dynein by the axonemal central apparatus.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2002 May;52(1):33-42. doi: 10.1002/cm.10031. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2002. PMID: 11977081
-
Regulation of flagellar dynein by an axonemal type-1 phosphatase in Chlamydomonas.J Cell Sci. 1996 Jul;109 ( Pt 7):1899-907. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.7.1899. J Cell Sci. 1996. PMID: 8832412
-
Regulation of Chlamydomonas flagellar dynein by an axonemal protein kinase.J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1683-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1683. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7798320 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of dynein-driven microtubule sliding by an axonemal kinase and phosphatase in Chlamydomonas flagella.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;32(2):106-9. doi: 10.1002/cm.970320207. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995. PMID: 8681389 Review.
-
Keeping an eye on I1: I1 dynein as a model for flagellar dynein assembly and regulation.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007 Aug;64(8):569-79. doi: 10.1002/cm.20211. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007. PMID: 17549744 Review.
Cited by
-
Composition and function of ciliary inner-dynein-arm subunits studied in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2021 Mar;78(3):77-96. doi: 10.1002/cm.21662. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 33876572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The axoneme: the propulsive engine of spermatozoa and cilia and associated ciliopathies leading to infertility.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2016 Feb;33(2):141-56. doi: 10.1007/s10815-016-0652-1. Epub 2016 Jan 29. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2016. PMID: 26825807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated control of axonemal dynein AAA(+) motors.J Struct Biol. 2012 Aug;179(2):222-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.02.013. Epub 2012 Mar 3. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22406539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An axonemal PP2A B-subunit is required for PP2A localization and flagellar motility.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011 Jul;68(7):363-72. doi: 10.1002/cm.20519. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21692192 Free PMC article.
-
Cryoelectron tomography reveals doublet-specific structures and unique interactions in the I1 dynein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 24;109(30):E2067-76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120690109. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22733763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannai H., Yoshimura M., Takahashi K., Shingyoji C.. 2000. Calcium regulation of microtubule sliding in reactivated sea urchin sperm flagella.J. Cell Sci. 113:831–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

