Management strategy for facial arteriovenous malformations
- PMID: 19753261
- PMCID: PMC2740518
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.44943
Management strategy for facial arteriovenous malformations
Abstract
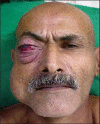
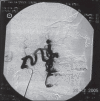
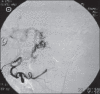
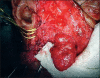
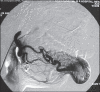
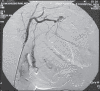
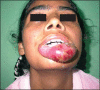
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are uncommon errors of vascular morphogenesis; haemodynamically, they are high-flow lesions. Approximately 50% of AVMs are located in the craniofacial region. Subtotal excision or proximal ligation of the feeding vessel frequently results in rapid progression of the AVMs. Hence, the correct treatment consists of highly selective embolisation (super-selective) followed by complete resection 24-48 hours later. We treated 20 patients with facial arteriovenous malformation by using this method. Most of the lesions (80%) were located within the cheek and lip. There were no procedure related complications and cosmetic results were excellent.
Keywords: Arteriovenous malformation; resection; super-selective embolisation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Kohout MP, Hansen M, Prebaz JJ, Mulliken JB. Arterio venous malformation of the head and neck: natural history and management. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;102:643–54. - PubMed
-
- Jackson IT, Carreno R, Potparic Z, Hussain K. Haemangiomas, vascular malformations and lympho-venous malformations: Classification and methods of treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993;91:1216–30. - PubMed
-
- Leikensohn JR, Epstein LI, Vasconez LO. Super-selective embolization and surgery of non-involuting haemangiomas and A-V malformations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981;68:143–52. - PubMed
-
- Holman E. The physiology of an arterio-venous fistula. Am J Surg. 1955;89:1101. - PubMed
-
- Brooks B. The treatment of traumatic arterio-venous fistula. South Med J. 1930;23:106.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

